Effects of stress on memory
[5][6] One class of stress hormone responsible for negatively affecting long-term, delayed recall memory is the glucocorticoids (GCs), the most notable of which is cortisol.
[9] Under normal circumstances, the hippocampus regulates the production of cortisol through negative feedback because it has many receptors that are sensitive to these stress hormones.
Studies considered the effects of both intrinsic and extrinsic stress on memory functions, using for both of them Pavlovian conditioning and spatial learning.
[12] Blood is redirected to the brain and major muscle groups, diverted away from energy consuming bodily functions unrelated to survival at the present time.
Vasopressin, also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), is synthesized by the neurons in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus and regulates fluid loss by manipulating the urinary tract.
This increase in blood pressure under stressful conditions ensures that muscles receive the oxygen that they need to be active and respond accordingly.
Chronic stress is the response to emotional pressure suffered for a prolonged period of time in which an individual perceives they have little or no control.
[19] One study used rats to show the effects of chronic stress on memory by exposing them to a cat for five weeks and being randomly assigned to a different group each day.
[20] Their stress was measured in a naturalistic setting by observing their open field behaviour, and the effect on memory was estimated using the radial arm water maze (RAWM).
It was found that the rats exposed to chronic psychosocial stress could not learn to adapt to new situations and environments, and had impaired memory on the RAWM.
[26] In contrast, for emotionally charged stimuli to be forgotten, the stressful exposure must be after encoding and retrieval must follow after a longer delay.
[clarification needed][5] Acute stress exposure induces the activation of different hormonal and neurotransmitters which effect the memory's working processes.
The study consisted on the participants viewing movie clips and pictures that belonged to two different categories: neutral or negative.
During a stressful time, a person's attention and emotional state may be affected, which could hinder the ability to focus while processing an image.
An example of this was when researchers found that stress experienced during crimes improved eyewitness memory, especially under the influence of Repeat Testing.
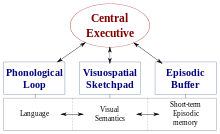
Working memory (WM), similar to STM, is the ability to temporarily store information in order to manipulate it for performing complex tasks, such as reasoning.
Anxiety has also been shown to adversely affect some of the components of WM, those being the phonological loop, the visuo-spatial sketchpad, and the central executive.
For instance, several studies have demonstrated that acute stress can impair working memory processing likely though reduced neural activity in the prefrontal cortex in both monkeys and humans.
[39] Basal cortisol levels are relatively low in the afternoon and much higher in the morning, which can alter the interaction and effects of stress hormones.
When stress is induced the memory will be susceptible to other influences,[42] such as suggestions from other people, or emotions unrelated to the event but present during recall.
[48] Inhibited reversal learning can be associated with the idea that subjects experiencing symptoms of anxiety frustrate easily and are unable to successfully adapt to a changing environment.
When the researchers inactivated that brain region by administering Muscimol to the females, no gender differences in classical conditioning were observed 24 hours later.
A few studies done in the past proved that PTSD can cause cognition and brain structure changes that involve verbal declarative memory deficits.
Children that have experienced child abuse may according to neuropsychological testing experience a deficit in verbal declarative memory functioning.
[59] The studies performed on the Vietnam veterans that suffer from PTSD show that there are hippocampal changes in the brain associated with this disorder.
People with social anxiety disorder have a constant, chronic fear of being watched and judged by peers and strangers, and of doing something that will embarrass them.
[64] Physical symptoms of the disorder include blushing, profuse sweating, trembling, nausea or abdominal distress, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, dizziness or lightheadedness, headaches, and feelings of detachment.
[71] Individuals with OCD may realize that their obsessions are not normal and try to stop their actions, but this only increases the person's anxiety towards the situation, and has an adverse effect.
Themes of obsessions include fear of germs or dirt, having things orderly and symmetrical, and sexual thoughts and images.
[71] Compulsions also follow the theme, including hand washing, cleaning, performing actions repeatedly, or extreme orderliness.