Endosome
Endosomes can be classified as early, sorting, or late depending on their stage post internalization.
LDL dissociates because of the slightly acidified environment of the early endosome, generated by a vacuolar membrane proton pump V-ATPase.
They also increase in size due to the homotypic fusion of early endosomes into larger vesicles.
Another unique identifying feature that differs between the various classes of endosomes is the lipid composition in their membranes.
Phosphatidyl inositol phosphates (PIPs), one of the most important lipid signaling molecules, is found to differ as the endosomes mature from early to late.
[16] These lipids on the surface of the endosomes help in the specific recruitment of proteins from the cytosol, thus providing them an identity.
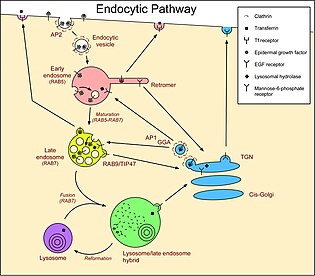
The inter-conversion of these lipids is a result of the concerted action of phosphoinositide kinases and phosphatases that are strategically localized[17] There are three main compartments that have pathways that connect with endosomes.
Also, in some circumstances, late endosomes/MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane instead of with lysosomes, releasing the lumenal vesicles, now called exosomes, into the extracellular medium.
There is no consensus as to the exact nature of these pathways, and the sequential route taken by any given cargo in any given situation will tend to be a matter of debate.
[18] In the opposite direction, retromer generates vesicles at early endosomes that carry molecules back to the Golgi.
Molecules that follow these pathways include the receptors for LDL, epidermal growth factor (EGF), and the iron transport protein transferrin.
LDL is released in endosomes because of the lower pH, and the receptor is recycled to the cell surface.
The activated EGFRs stimulate their own ubiquitination, and this directs them to lumenal vesicles (see below) and so they are not recycled to the plasma membrane.
[26] Molecules that follow these pathways include LDL and the lysosomal hydrolases delivered by mannose-6-phosphate receptors.
Also, the transmembrane EGFRs, bound to EGF, are tagged with ubiquitin and are therefore sorted into lumenal vesicles by the ESCRTs.