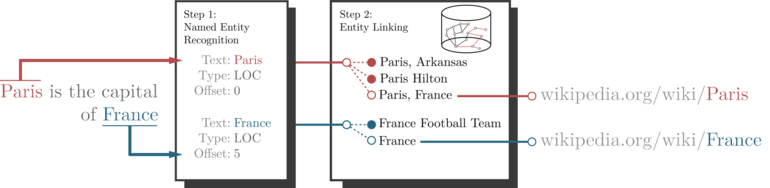
Entity linking
Even worse, the search engine might produce spurious matches (or false positives (FP)), such as retrieving documents referring to "France" as a country.
However, these techniques do not allow the same fine-grained control that is offered by entity linking, as they will return other documents instead of creating high-level representations of the original one.
For example, obtaining schematic information about "Paris", as presented by Wikipedia infoboxes would be much less straightforward, or sometimes even unfeasible, depending on the query complexity.
[25] Broadly speaking, modern entity linking systems can be divided into two categories: Often entity linking systems use both knowledge graphs and textual features extracted from, for example, the text corpora used to build the knowledge graphs themselves.
The final step is a collective disambiguation by comparing binary vectors of hand-crafted features each entity's context.
Then, the best link among the candidates is chosen with a ranking support vector machine (SVM) that uses linguistic features.
Like most entity linking systems, it has two steps: an initial candidate selection, and ranking using linear SVM.
The seminal approach of Milne and Witten uses supervised learning using the anchor texts of Wikipedia entities as training data.
Han et al. propose the creation of a disambiguation graph (a subgraph of the knowledge base which contains candidate entities).
Mathematical expressions (symbols and formulae) can be linked to semantic entities (e.g., Wikipedia articles[32] or Wikidata items[33]) labeled with their natural language meaning.
[34][33] The math entity linking process can be facilitated and accelerated through annotation recommendation, e.g., using the "AnnoMathTeX" system that is hosted by Wikimedia.
[35][36][37] To facilitate the reproducibility of Mathematical Entity Linking (MathEL) experiments, the benchmark MathMLben was created.
[33] Furthermore, for two large corporae from the arXiv[40] and zbMATH[41] repository distributions of mathematical notation were examined.