Environmental health
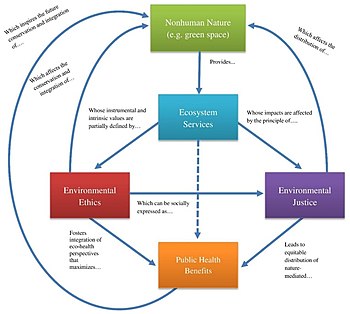
[4] A 1990 WHO document states that environmental health, as used by the WHO Regional Office for Europe, "includes both the direct pathological effects of chemicals, radiation and some biological agents, and the effects (often indirect) on health and well being of the broad physical, psychological, social and cultural environment, which includes housing, urban development, land use and transport.
This can in turn be used to develop and implement environmental health policy that, for example, regulates chemical emissions, or imposes standards for proper sanitation.
[26] In the United States, Superfund sites created by various companies have been found to be hazardous to human and environmental health in nearby communities.
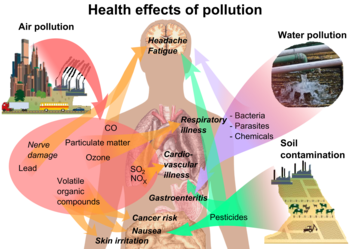
[28] Air pollution is the contamination of an atmosphere due to the presence of substances that are harmful to the health of living organisms, the environment or climate.
[32][33] These pollutants are responsible for the burning of fuel, which can release harmful particles into the air that humans and other living organisms can inhale or ingest.
[34] Air pollution is associated with adverse health effects like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, cancer, related illnesses, and even death.
The country implemented a clean air policy to reduce the road transport sector, which is responsible for 85% of particulate matter of less than 2.5 microns (PM2.5) total emissions and 72% of particulate matter of less than 10 microns (PM10)[38] Most successful policies were: Household air pollution contributes to diseases that kill almost 4.3 million people every year.
[45][46] These extreme weather events can increase the likelihood of undernutrition, mortality, food insecurity, and climate-sensitive infectious diseases in vulnerable populations.
[48] Climate impacts can affect exposure to water-borne pathogens through increased rates of runoff, frequent heavy rains, and the effects of severe storms.
[49] Extreme weather events and storm surges can also exceed the capacity of water infrastructure, which can increase the likelihood that populations will be exposed to these contaminants.
These events can lead to vulnerability in the form of housing affordability stress, lower household income, lack of community attachment, grief, and anxiety around another disaster occurring.
These marginalized groups are frequently put next to pollution sources like major roadways, toxic waste sites, landfills, and chemical plants.
[52] In a 2021 study, it was found that racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States are exposed to disproportionately high levels of particulate air pollution.
[56] Noise pollution is also responsible for many reported cases of hearing loss, tinnitus, and other forms of hypersensitivity(stress/irritability) or lack thereof to sound(present or subconscious from continuous exposure).
[57] This is consistent with research that suggests that children who are exposed to regular aircraft noise "have inadequate performance on standardised achievement tests.
Access to safe drinking water is considered a "basic human need for health and well-being" by the United Nations.
[71] With the interest of environmental health in mind, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act was passed in the United States in 1976 that covered how to properly manage hazardous waste.
These professionals work in various sectors, including government agencies, private industry, consulting firms, and non-profit organizations, all with the common goal of ensuring the safe handling of hazardous materials and waste.
These positions include but are not limited to Environmental Health and Safety Specialists, Waste collectors, Medical Professionals, and Emergency Responders.
The tiny particles known as microplastics (MPs), have been found in various environmental and biological matrices, including air, water, food, and human tissues.
While visible pollution caused by larger plastic items is well-documented, the hidden threat posed by nanoplastics remains under-explored.
These particles originate from the degradation of larger plastics and are now found in various environmental matrices, including water, soil, and air.
Given their minute size, nanoplastics can penetrate biological barriers and accumulate in human tissues, potentially leading to adverse health effects.
[78][79] Plastics continue to accumulate in landfills and oceans, leading to pollution that negatively affects both human and animal health.
Studies indicate that humans ingest significant amounts of microplastics daily through food, especially seafood[80] and inhalation, with estimates ranging from 39,000 to 52,000 particles per person annually.
Most exposure is accidental, and exposure can happen through:[86] The Toxicology and Environmental Health Information Program (TEHIP)[87] is a comprehensive toxicology and environmental health web site, that includes open access to resources produced by US government agencies and organizations, and is maintained under the umbrella of the Specialized Information Service at the United States National Library of Medicine.
TOXMAP's chemical and environmental health information is taken from the NLM's Toxicology Data Network (TOXNET)[91] and PubMed, and from other authoritative sources.
This was epitomized by Sir Edwin Chadwick, who was instrumental in the repeal of the poor laws, and in 1884 was the founding president of the Association of Public Sanitary Inspectors, now called the Chartered Institute of Environmental Health.