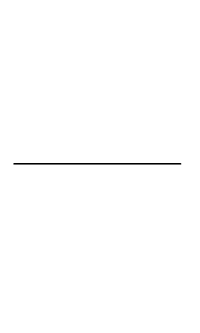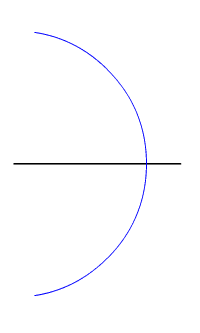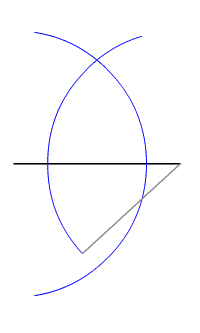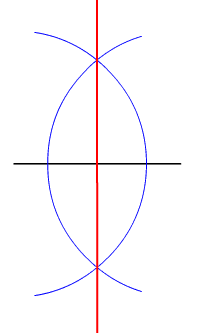Equidistant
For a triangle the circumcentre is a point equidistant from each of the three vertices.
This result can be generalised to cyclic polygons: the circumcentre is equidistant from each of the vertices.
A point on the axis of symmetry of a kite is equidistant between two sides.
A parabola is the set of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point (the focus) and a fixed line (the directrix), where distance from the directrix is measured along a line perpendicular to the directrix.
In hyperbolic geometry the set of points that are equidistant from and on one side of a given line form a hypercycle (which is a curve, not a line).