Equivalent dose
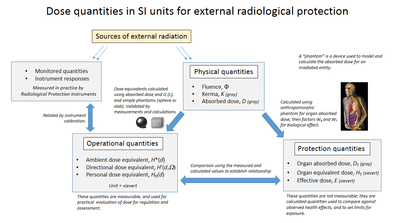
For applications in radiation protection and dosimetry assessment, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) and the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) have published recommendations and data on how to calculate equivalent dose from absorbed dose.
[6] This takes into account the contributions of the varying biological effect of different radiation types.
[8] Some regulators, notably the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) and the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission continue to use the old terminology of quality factors and dose equivalent, even though the underlying calculations have changed.
[10] These proposals will need to go through the following stages: The SI unit of measure for equivalent dose is the sievert, defined as one Joule per kg.
[12] Equivalent dose HT is used for assessing stochastic health risk due to external radiation fields that penetrate uniformly through the whole body.
Committed equivalent dose, H T(t) is the time integral of the equivalent dose rate in a particular tissue or organ that will be received by an individual following intake of radioactive material into the body by a Reference Person, where s is the integration time in years.
[16] The International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) and the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission continue to use the old terminology of quality factors and dose equivalent.
[17] The radiation weighting factors for neutrons are also different between US NRC and the ICRP - see accompanying diagram.