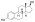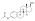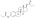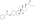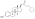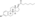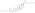Estradiol valerate
[13] Low-dose oral estradiol valerate (2–6 mg/day) has been used in the treatment of breast cancer in women who were previously treated with and benefited from but acquired resistance to aromatase inhibitors as well.
[13] Elsewhere in the world, oral estradiol valerate is similarly approved for the treatment of symptoms associated with menopause or hypoestrogenism due to castration in women.
[14] Such symptoms may include hot flashes, outbreaks of sweat, sleep disturbances, depressive moods, irritability, headaches, and dizziness.
[14] Estradiol valerate by intramuscular injection is usually used at a dosage of 10 to 20 mg every 4 weeks in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism, castration, or primary ovarian failure in women.
[36] Estradiol valerate is usually used in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer in men at a dosage of 30 mg or more every 1 to 2 weeks by intramuscular injection.
[39][19][40][41] In the United States, it is specifically available in formulations of 10, 20, and 40 mg/mL in oil solution (as Delestrogen, as well as generics).
[39][26][27][28][1] Intramuscular estradiol valerate is also marketed at a concentration of 4 mg/mL in combination with the weak androgen and neurosteroid prasterone enanthate (DHEA enanthate) and with the androgen testosterone enantate for use in menopausal hormone therapy, but the latter formulation has been discontinued.
Examples of such side effects include breast tenderness and enlargement, nausea, bloating, edema, headache, and melasma.
[62] Estradiol valerate has been used at very high doses of 40 to 100 mg once per week in women and men, without overt signs of acute toxicity observed.
[101][102] Oral estradiol valerate at 6 mg/day has been found to increase SHBG levels by 2.5- to 3-fold in transgender women.
[103][104] For comparison, combined birth control pills containing ethinylestradiol and a progestin with minimal androgenic or antiandrogenic activity have been found to increase SHBG levels by about 3- to 4-fold.
[4] This is also notably true for effects on hepatic protein synthesis (e.g., of SHBGTooltip sex hormone-binding globulin), again after differences in molecular weight between the two compounds are considered.
[107] Estradiol valerate has been studied by sublingual administration in premenopausal women for the purpose of cycle control and ovulation suppression in egg donation and surrogacy.
[116] The administration of 2 mg oral micronized estradiol valerate tablets (Progynova, Schering) sublingually 3 or 4 times per day has been found to result in circulating estradiol levels of about 290 pg/mL to 460 pg/mL in premenopausal women (time of measurements not given).
[114][115][117] In contrast to oral administration, the bioavailability of estradiol valerate is complete (i.e., 100%) via intramuscular injection.
[6][4][5] Due to the far greater bioavailability of intramuscular estradiol valerate relative to oral, the former is substantially stronger (in terms of potency) than the latter.
[4] As an example, a single 4 mg intramuscular injection is said to be approximately equivalent to 2 mg/day of the medication administered orally over the course of 3 weeks.
[9] Α couple of older studies from the 1980s with sample sizes of only 2 or 3 individuals reported an elimination half-life of 4 to 5 days.
[10] Other studies have found that larger doses of intramuscular estradiol valerate exceeding 20 mg have a duration of more than 15 days.
[10] A third study, in contrast to the preceding study, found that a single 10 mg intramuscular injection of estradiol valerate resulted in maximal estradiol levels of 506 to 544 pg/mL and maximal estrone levels of 205 to 219 pg/mL in postmenopausal women.
[4][120] The bioavailability and metabolism of estradiol valerate does not differ with intravenous versus intramuscular injection.
[19][133] It was synthesized and studied, along with a variety of other estradiol esters, by Karl Junkmann of Schering AG in 1953.
[20][21][136] In 1966, oral estradiol valerate was introduced by Schering for medical use in Europe under the brand name Progynova.
[23][24][148] Estradiol valerate has been marketed under the brand names Altadiol, Androtardyl-Oestradiol, Ardefem, Climaval, Cyclabil, Cyclocur, Deladiol, Delahormone Unimatic, Delestrogen, Delestrogen 4X, Depogen, Diol-20, Dioval, Ditate, Dura-Estate, Dura-Estradiol, Duratrad, Duragen, Estate, Estra-L, Estradiol Depot, Estraval, Estraval Depot, Estraval PA, Estravel, Femogen, Femogex, Gynogen L.A., Gynokadin, Lastrogen, Menaval, Merimono, Neofollin, Nuvelle, Oestrogynal, Ostrin Depo, Pelanin, Pharlon, Postoval, Primogyna, Primogyn, Primogyn Depot, Progynon, Progynon Depot, Progynova, Repestrogen, Repo-Estra, Reposo-E, Retestrin, Ronfase, Span-Est, Testaval, and Valergen, among others.