Eurasian Economic Community
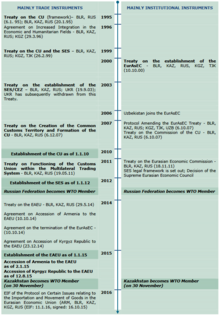
[3] The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on 29 March 1996,[4] with the treaty on the establishment of the Eurasian Economic Community signed on 10 October 2000 in Kazakhstan's capital Astana by Presidents Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus, Nursultan Nazarbayev of Kazakhstan, Askar Akayev of Kyrgyzstan, Vladimir Putin of Russia, and Emomali Rahmon of Tajikistan.
The four freedoms of movement modelled after the European Union (goods, capital, services, and people) were fully implemented by 25 January 2012, with the formation of the Eurasian Economic Space.
[6][7][8] On 10 October 2014, an agreement on the termination of the Eurasian Economic Community was signed in Minsk after a session of the Interstate Council of the EAEC.
[citation needed] While the Eurasian Economic Union effectively replaces the community, membership negotiations with Tajikistan are still ongoing.
[9] Every member state has a certain number of votes: Some boards and commissions within the Integration Committee: The Secretariat is headed by the Secretary General of the Eurasec, the highest Community official, appointed by the interstate Council.
The Common Economic Space would involve a supranational commission on trade and tariffs that would be based in Kyiv, would initially be headed by a representative of Kazakhstan, and would not be subordinate to the governments of the four nations.
On March 1, 2010, the first deputy head of the presidential administration of newly elected Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych, Iryna Akymova stated that Ukraine does not intend to join the Customs Union of Russia, Kazakhstan and Belarus in the near future "Since the customs union contradicts and will greatly complicate Ukraine's membership in the WTO".
[8] Forming a customs union between EurAsEC member states became a top priority from Spring 2008, when the EU announced its Eastern Partnership.
Since that time, there has been discord between the EU and Russia with both sides accusing the other of attempting to carve out spheres of influence over the countries at issue (Belarus, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine).
Boiled down to its essence, Russia has offered EurAsEC members access to its markets (i.e., for Kazakhstan) and lower energy prices (i.e., Belarus, Ukraine).
Belarusian President, Alexander Lukashenko said: "The Eurasian Economic Community will establish a fund of $10 billion to deal with the financial crisis."
Members wanted the EurAsEC to become a viable economic bloc between the powerful EU in the West, and the growing economies in the east, which established the ASEAN).
[16] Although Uzbekistan has not given any official reason, many interpret the move as an attempt to revive stagnating relations with the West and to assertively dismissing Russian influence.
[17] Other views interpret Uzbekistan's move as a nationalist attempt in response to an economic crisis, in order to regain tighter control over its economy.