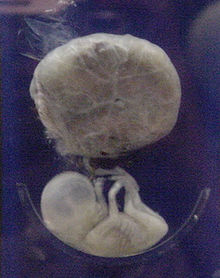
Fetus
: fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn mammalian offspring that develops from an embryo.
Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus.
However, in general a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional, and some may not yet be situated in their final anatomical location.
[2] The predominant British, Irish, and Commonwealth spelling is foetus, except in medical usage, where fetus is preferred.
[9] The heart, hands, feet, brain, and other organs are present, but are only at the beginning of development and have minimal operation.
If given expert postnatal care, some preterm babies weighing less than 500 g (1 lb 2 oz) may survive, and are referred to as extremely low birth weight or immature infants.
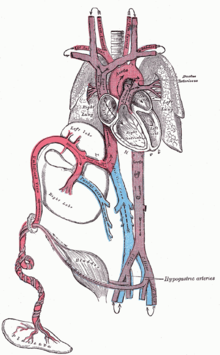
A functional circulatory system is a biological necessity since mammalian tissues can not grow more than a few cell layers thick without an active blood supply.
The blood from the lungs travels through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium, producing an increase in pressure that pushes the septum primum against the septum secundum, closing the foramen ovale and completing the separation of the newborn's circulatory system into the standard left and right sides.
[26] A developing fetus is highly susceptible to anomalies in its growth and metabolism, increasing the risk of birth defects.
Studies show that supplementation of the person's diet with folic acid reduces the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
[28] Smoking during pregnancy may also lead to miscarriages and low birth weight (2,500 grams (5 pounds 8 ounces).
X-rays are known to have possible adverse effects on the development of the fetus, and the risks need to be weighed against the benefits.
An abdominal pregnancy can result in the death of the fetus and where this is rarely not resolved it can lead to its formation into a lithopedion.
"[31][32] However, developmental neurobiologists argue that the establishment of thalamocortical connections (at about 6+1⁄2 months) is an essential event with regard to fetal perception of pain.
[35][36][37] In the United States, for example, anti-abortion advocates have proposed legislation that would require providers of abortions to inform pregnant women that their fetuses may feel pain during the procedure and that would require each person to accept or decline anesthesia for the fetus.
[41] However, the anatomy of the area surrounding a fetus is different in litter-bearing animals compared to humans: each fetus of a litter-bearing animal is surrounded by placental tissue and is lodged along one of two long uteri instead of the single uterus found in a human female.
In contrast, precocial animals are born with open eyes, have hair or down, have large brains, and are immediately mobile and somewhat able to flee from, or defend themselves against, predators.
[42] The duration of gestation in placental mammals varies from 18 days in jumping mice to 23 months in elephants.
[43] Generally speaking, fetuses of larger land mammals require longer gestation periods.
However, carrying fetuses exerts costs on the mother, who must take on extra food to fuel the growth of her offspring, and whose mobility and comfort may be affected (especially toward the end of the fetal stage).
In some instances, the presence of a fetal stage may allow organisms to time the birth of their offspring to a favorable season.