Foot drop
Foot drop may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of muscle weakness or paralysis, and it can occur in one or both feet.
Foot drop can be caused by nerve damage alone or by muscle or spinal cord trauma, abnormal anatomy, toxins, or disease.
Diseases that can cause foot drop include trauma to the posterolateral neck of fibula, stroke,[1][2][3][4] amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, poliomyelitis, Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, hereditary spastic paraplegia, Guillain–Barré syndrome, Welander distal myopathy, Friedreich's ataxia, chronic compartment syndrome, and severe nerve entrapment.
Other gaits such as a wide outward leg swing (to avoid lifting the thigh excessively or to turn corners in the opposite direction of the affected limb) may also indicate foot drop.
[9] Patients with painful disorders of sensation (dysesthesia) of the soles of the feet may have a similar gait but do not have foot drop.
[citation needed] Foot drop is rarely the result of a pathology involving the muscles or bones that make up the lower leg.
Other causes of foot drop are diabetes (due to generalized peripheral neuropathy), trauma, motor neuron disease (MND), adverse reaction to a drug or alcohol, and multiple sclerosis.
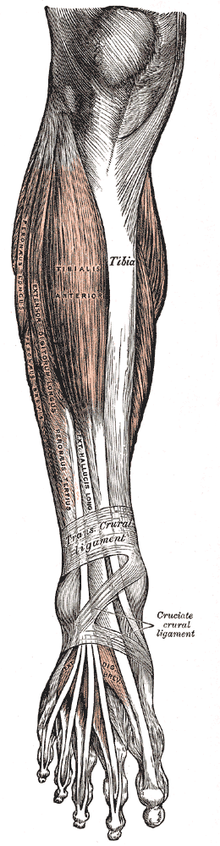
The muscles that are used in plantar flexion are innervated by the tibial nerve and often develop tightness in the presence of foot drop.
If the foot drop is the result of a peripheral nerve injury, a window for recovery of 18 months to 2 years is often advised.
[citation needed] Non-surgical treatments for spinal stenosis include a suitable exercise program developed by a physical therapist, activity modification (avoiding activities that cause advanced symptoms of spinal stenosis), epidural injections, and anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or aspirin.
Spinal fusion surgery may be required to treat this condition, with many patients improving their function and experiencing less pain.
If pain medication, progressive activity, or a brace or support does not help with the fracture, two minimally invasive procedures - vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty - may be options.
Ankles can be stabilized by lightweight orthoses, available in molded plastics as well as softer materials that use elastic properties to prevent foot drop.
Often, individuals with foot drop prefer to use a compensatory technique like steppage gait or hip hiking as opposed to a brace or splint.
FES is applied to lower extremities for improving functional walking in stroke patients; for the correction of foot drop.
Another method uses a cuff placed around the patient's ankle, and a topside spring and hook installed under the shoelaces.