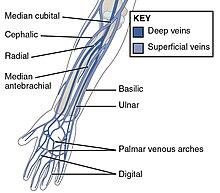
Forearm
These veins can be used for cannularisation or venipuncture, although the cubital fossa is a preferred site for getting blood.
The bones of the forearm are the radius (located on the lateral side) and the ulna (located on the medial side) Proximally, the head of the radius articulates with the capitulum of the humerus and the radial notch of the ulna at the elbow.
For treatment of children with torus fractures of the forearm splinting appears to work better than casting.
[7] Genetically determined disorders like hereditary multiple exostoses can lead to hand and forearm deformities.
Hereditary multiple exostoses is due growth disturbance of the epiphyses of the radius and ulna, the two bones of the forearm.