Free spectral range
Free spectral range (FSR) is the spacing in optical frequency or wavelength between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element.
[1] The FSR is not always represented by
, but instead is sometimes represented by just the letters FSR.
The reason is that these different terms often refer to the bandwidth or linewidth of an emitted source respectively.
The free spectral range (FSR) of a cavity in general is given by [2] or, equivalently, These expressions can be derived from the resonance condition
in Taylor series.
is the wavevector of the light inside the cavity,
are the wavevector and wavelength in vacuum,
is the refractive index of the cavity and
is the round trip length of the cavity (notice that for a standing-wave cavity,
is equal to twice the physical length of the cavity).
, the FSR (in wavelength) is given by being
is the group index of the media within the cavity.
is the speed of light in vacuum.
If the dispersion of the material is negligible, i.e.
, then the two expressions above reduce to and A simple intuitive interpretation of the FSR is that it is the inverse of the roundtrip time
is the vacuum wavelength of light.
For a linear cavity, such as the Fabry-Pérot interferometer[3] discussed below,
is the distance travelled by light in one roundtrip around the closed cavity, and
The free spectral range of a diffraction grating is the largest wavelength range for a given order that does not overlap the same range in an adjacent order.
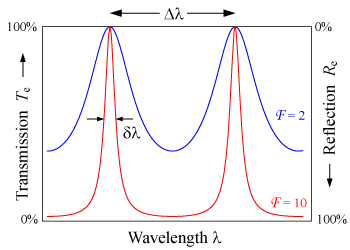
lie at the same angle, then In a Fabry–Pérot interferometer[3] or etalon, the wavelength separation between adjacent transmission peaks is called the free spectral range of the etalon and is given by where λ0 is the central wavelength of the nearest transmission peak, n is the index of refraction of the cavity medium,
More often FSR is quoted in frequency, rather than wavelength units: The FSR is related to the full-width half-maximum δλ of any one transmission band by a quantity known as the finesse: where
is the coefficient of finesse, and R is the reflectivity of the mirrors.