Game theory
Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics.
[3] The second edition provided an axiomatic theory of expected utility, which allowed mathematical statisticians and economists to treat decision-making under uncertainty.
Though he did not refer to it as such, he presented a solution that is the Nash equilibrium of the game in his Recherches sur les principes mathématiques de la théorie des richesses (Researches into the Mathematical Principles of the Theory of Wealth).
[10][11] Von Neumann's original proof used Brouwer's fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics.
The first mathematical discussion of the prisoner's dilemma appeared, and an experiment was undertaken by mathematicians Merrill M. Flood and Melvin Dresher, as part of the RAND Corporation's investigations into game theory.
In the 1970s, game theory was extensively applied in biology, largely as a result of the work of John Maynard Smith and his evolutionarily stable strategy.
In 2007, Leonid Hurwicz, Eric Maskin, and Roger Myerson were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics "for having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory".
In 2012, Alvin E. Roth and Lloyd S. Shapley were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics "for the theory of stable allocations and the practice of market design".
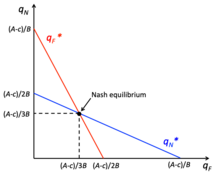
It is different from non-cooperative game theory which focuses on predicting individual players' actions and payoffs by analyzing Nash equilibria.
Due to the probability involved, the analysis of this situation requires to understand the player's preference for the draw, even though people are only interested in pure strategic equilibrium.
[35] Research in artificial intelligence has addressed both perfect and imperfect information games that have very complex combinatorial structures (like chess, go, or backgammon) for which no provable optimal strategies have been found.
They may be modeled using similar tools within the related disciplines of decision theory, operations research, and areas of artificial intelligence, particularly AI planning (with uncertainty) and multi-agent system.
[42] (See Black swan theory for more discussion on this kind of modeling issue, particularly as it relates to predicting and limiting losses in investment banking.)
General models that include all elements of stochastic outcomes, adversaries, and partial or noisy observability (of moves by other players) have also been studied.
The term metagame analysis is also used to refer to a practical approach developed by Nigel Howard,[43] whereby a situation is framed as a strategic game in which stakeholders try to realize their objectives by means of the options available to them.
Mean field game theory is the study of strategic decision making in very large populations of small interacting agents.
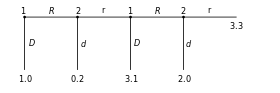
The way this particular game is structured (i.e., with sequential decision making and perfect information), Player 1 "moves" first by choosing either F or U (fair or unfair).
Evolutionary game theory includes both biological as well as cultural evolution and also models of individual learning (for example, fictitious play dynamics).
[108] CIPS and TWS Partners have conducted a series of surveys designed to explore the understanding, awareness and application of game theory among procurement professionals.
In terms of types of games, both cooperative as well as non-cooperative, normal-form as well as extensive-form, and zero-sum as well as non-zero-sum are used to model various project management scenarios.
[citation needed] A game-theoretic explanation for democratic peace is that public and open debate in democracies sends clear and reliable information regarding their intentions to other states.
War may result from asymmetric information; two countries may have incentives to mis-represent the amount of military resources they have on hand, rendering them unable to settle disputes agreeably without resorting to fighting.
The tool,[119] for example, automates the transformation of public vulnerability data into models, allowing defenders to synthesize optimal defence strategies through Stackelberg equilibrium analysis.
This approach enhances cyber resilience by enabling defenders to anticipate and counteract attackers’ best responses, making game theory increasingly relevant in adversarial cybersecurity environments.
Ho et al. provide a broad summary of game theory applications in defence, highlighting its advantages and limitations across both physical and cyber domains.
Examples can be found in species ranging from vampire bats that regurgitate blood they have obtained from a night's hunting and give it to group members who have failed to feed, to worker bees that care for the queen bee for their entire lives and never mate, to vervet monkeys that warn group members of a predator's approach, even when it endangers that individual's chance of survival.
Hamilton's rule explains the evolutionary rationale behind this selection with the equation c < b × r, where the cost c to the altruist must be less than the benefit b to the recipient multiplied by the coefficient of relatedness r. The more closely related two organisms are causes the incidences of altruism to increase because they share many of the same alleles.
[d] Other authors have attempted to use evolutionary game theory in order to explain the emergence of human attitudes about morality and corresponding animal behaviors.
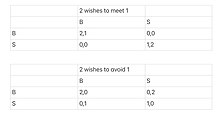
The "battle of the sexes" is a term used to describe the perceived conflict between men and women in various areas of life, such as relationships, careers, and social roles.
For instance, in some romantic comedies, the male and female protagonists are shown as having opposing views on love and relationships, and they have to overcome these differences in order to be together.