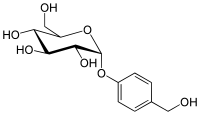
Gastrodin
It has been isolated from the rhizomes of two orchid species, Gastrodia elata and Galeola faberi.
[1] It can also be produced by biotransformation of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde by Datura tatula cell cultures.
[2] G. elata rhizome is a herb used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat headache, and it is standardized in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia by gastrodin and gastrodigenin content.
[3] In line with this traditional use, gastrodin and its acetyl derivative are used in China as an over-the-counter drug to treat neurasthenia, headache, and migraine.
A Chinese literature review considers it useful for a range of central nervous system disorders, with the evidence coming from mostly Chinese researches.