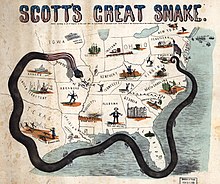
Winfield Scott
After capturing the port city of Veracruz, he defeated Mexican General Antonio López de Santa Anna's armies at the Battles of Cerro Gordo, Contreras, and Churubusco.
He then captured Mexico City, after which he maintained order in the Mexican capital and indirectly helped envoy Nicholas Trist negotiate the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which brought an end to the war.
[17] Later that year, Scott attempted to establish a legal practice in South Carolina but was unable to obtain a law license because he did not meet the state's one-year residency requirement.
[18] In early 1808, President Thomas Jefferson asked Congress to authorize an expansion of the United States Army after the British announced an escalation of their naval blockade of France, thereby threatening American shipping.
[30] After the duel, Scott returned to Virginia, where he spent the year studying military tactics and strategy,[22] and practicing law in partnership with Benjamin Watkins Leigh.
[37] While Izard continued to lead recruitment efforts, Scott led two companies north to join General Stephen Van Rensselaer's militia force, which was preparing for an invasion of the Canadas.
Scott led an artillery bombardment that supported an American crossing of the Niagara River, and he took overall command of U.S. forces at Queenston after Colonel Solomon Van Rensselaer was badly wounded.
[42] As part of a prisoner exchange, Scott was released in late November; upon his return to the United States, he was promoted to colonel and appointed to command the 2nd Artillery Regiment.
With help from United States Navy elements commanded by Isaac Chauncey and Oliver Hazard Perry, he led U.S. troops to land behind the fort, forcing its surrender.
Despite this success, the campaign fell apart after the American defeat at the Battle of Crysler's Farm and after Wilkinson (who had taken command of the front in August) and Hampton failed to cooperate on a strategy to take Montreal.
[61] Scott's Society of the Cincinnati insignia, made by silversmiths Thomas Fletcher and Sidney Gardiner of Philadelphia, was a one-of-a-kind, solid gold eagle measuring nearly three inches in height.
Scott and Governor John Reynolds concluded the Black Hawk Purchase with Chief Keokuk and other Native American leaders, opening up much of present-day Iowa to settlement by whites.
[86] Scott traveled to Charleston, South Carolina, the center of the nullification movement, where he strengthened federal forts but also sought to cultivate public opinion away from secession.
[100] In late 1838, a new crisis known as the Aroostook War broke out over a dispute regarding the border between Maine and Canada, which had not been conclusively settled in previous treaties between Britain and the United States.
[103] Scott's success in preventing war with Canada under Van Buren confirmed his popularity with the broad public, and in early 1839, newspapers began to mention him as a candidate for the presidential nomination at the 1839 Whig National Convention.
With Congress unwilling to establish the rank of lieutenant general for Democratic Senator Thomas Hart Benton, Polk reluctantly turned to Scott to command the invasion.
[120] While Scott prepared the invasion, Taylor inflicted what the U.S. characterized as a crushing defeat on the army of Mexican President Antonio López de Santa Anna at the Battle of Buena Vista.
[132] In the Battle of Cerro Gordo, Pillow's force was largely ineffective, but Twiggs and Colonel William S. Harney captured the key Mexican position of El Telegrafo in hand-to-hand fighting.
Because Mexico City lacked walls and was essentially indefensible, Santa Anna sought to defeat Scott in a pitched battle, choosing to mount a defense near the Churubusco River several miles south.
[136] The Battle of Contreras began on the afternoon of August 19, when the Mexican army under General Gabriel Valencia attacked and pushed back an American detachment charged with building a road.
[141] While negotiations continued, Scott faced a difficult issue in the disposition of 72 members of Saint Patrick's Battalion who had deserted from the U.S. Army and were captured while fighting for Mexico.
[154] Congress became engaged in a divisive debate over the status of slavery in the territories, and Scott joined with Whig leaders Henry Clay and Daniel Webster in advocating for the passage of what became known as the Compromise of 1850.
[158] The 1852 Whig National Convention convened on June 16, and Southern delegates won approval of a party platform endorsing the Compromise of 1850 as a final settlement of the slavery question.
[161] The 1852 Democratic National Convention nominated dark horse candidate Franklin Pierce, a Northerner sympathetic to the Southern view on slavery who had served under Scott as a brigadier general during the Mexican War.
[162] Pierce had resigned from the U.S. Senate in 1842, and had briefly held only the minor office of United States Attorney for the District of New Hampshire since then, but emerged as a compromise candidate partly because he served under Scott in the Mexican–American War.
If necessary, I shall plant cannon at both ends of Pennsylvania Avenue, and if any of the Maryland or Virginia gentlemen who have become so threatening and troublesome show their heads or even venture to raise a finger, I shall blow them to hell.
"[198] Following a strategy similar to Scott's Anaconda Plan, Grant led the Union to victory, and Lee's Army of Northern Virginia surrendered in April 1865.
"[202] Biographer John Eisenhower writes that Scott "was an astonishing man" who was the country's "most prominent general" between the retirement of Andrew Jackson in 1821 and the onset of the Civil War in 1861.
"[206] Fanny Crosby, the hymn writer, recalled that Scott's "gentle manner did not indicate a hero of so many battles; yet there was strength beneath the exterior appearance and a heart of iron within his breast.
"[207] In addition to his reputation as a tactician and strategist, Scott was also noteworthy for his concern about the welfare of his subordinates, as demonstrated by his willingness to risk his career in the dispute with Wilkinson over the Louisiana bivouac site.