Geography of Australia
The geography of the continent is extremely diverse, ranging from the snow-capped mountains of the Australian Alps and Tasmania to large deserts, tropical and temperate forests, grasslands, heathlands and woodlands.
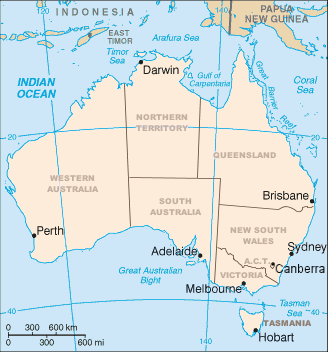
Properly called the Commonwealth of Australia, its territory consists of the entire continent and smaller outlying islands.
This makes it the sixth-largest country in the world by area of jurisdiction, which comprises 7,686,850 km2 (2,967,910 sq mi) (including Lord Howe Island and Macquarie Island), which is slightly smaller than the 48 states of the contiguous United States and 31.5 times larger than that of the United Kingdom.
These Eastern Australian temperate forests have the greatest relief, the most rainfall, the most abundant and varied flora and fauna, and the densest human settlement.
The large and mountainous island of Tasmania, also a State of Australia, lies south of the south-eastern corner of the Australian mainland.
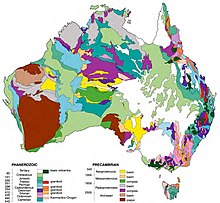
[6][7] Australia is the lowest, flattest, and oldest continental landmass on Earth[8] and it has had a relatively stable geological history.
Charles Rowland Twidale estimates that between 10% and 20% of Australia's modern landscapes formed during the Mesozoic when the continent was part of Gondwana.
The headwaters of some waterways are located in tropical regions where summer rains create a high rate of discharge.
Flood events drastically alter the dry environment; thus the ecology of central Australia has had to adapt to the boom and bust cycle.
Due to various geographical features of Australia, almost 80% of the Australian population live within 25 km of the coast,[13] where most of its capital cities and suburban satellites exist.
Rainfall is highly variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation.
A 2005 study by Australian and American researchers investigated the desertification of the interior, and suggested that one explanation was related to human settlers who arrived about 50,000 years ago.
This is due to the unique flora that exists, which is highly flammable, and some species actually requiring fire to regenerate and spread.
They are the deadliest natural disasters in Australia, accounting for more deaths than bushfires, cyclones, earthquakes, floods and severe storms combined.
The prominence and severity of droughts in Australia has increased in recent times due to accelerated climate change.
[26] As Australia is the driest inhabited continent, such droughts can limit the streamflow of the few major rivers in the country, creating a myriad of knock-on effects.
While Australia is not a seismically active zone, it does experience small scale earthquakes, caused by compressive stress built up over time, in the interior of the Australian tectonic plate.
[28] Current environmental issues include: soil erosion from overgrazing, industrial development, urbanization, and poor farming practices; soil salinity rising due to the use of poor quality water; desertification (partly as a result of the introduction by European settlers of rabbits); introduced pest species; clearing for agricultural purposes threatens the natural habitat of many unique animal and plant species; the Great Barrier Reef off the northeast coast, the largest coral reef in the world, is threatened by increased shipping and its popularity as a tourist site; limited natural fresh water resources; and threats from invasive species.