Geophysics
Geophysicists, who usually study geophysics, physics, or one of the Earth sciences at the graduate level, complete investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines.
The term geophysics classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields ; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation.
[3] However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.
[3][4][5][6][7][8] Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins date back to ancient times.
Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle.
Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection.
To provide a more clear idea on what constitutes geophysics, this section describes phenomena that are studied in physics and how they relate to the Earth and its surroundings.
Geophysicists also investigate the physical processes and properties of the Earth, its fluid layers, and magnetic field along with the near-Earth environment in the Solar System, which includes other planetary bodies.
The geoid would be the global mean sea level if the oceans were in equilibrium and could be extended through the continents (such as with very narrow canals).
[21] Relative to the solid Earth, the ionization of the planet's atmosphere is a result of the galactic cosmic rays penetrating it, which leaves it with a net positive charge.
Dawn chorus is believed to be caused by high-energy electrons that get caught in the Van Allen radiation belt.
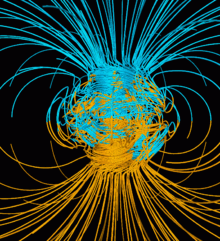
In the highly conductive liquid iron of the outer core, magnetic fields are generated by electric currents through electromagnetic induction.
[26] The Earth's field is roughly like a tilted dipole, but it changes over time (a phenomenon called geomagnetic secular variation).
These geomagnetic reversals, analyzed within a Geomagnetic Polarity Time Scale, contain 184 polarity intervals in the last 83 million years, with change in frequency over time, with the most recent brief complete reversal of the Laschamp event occurring 41,000 years ago during the last glacial period.
[24] Radioactive decay accounts for about 80% of the Earth's internal heat, powering the geodynamo and plate tectonics.
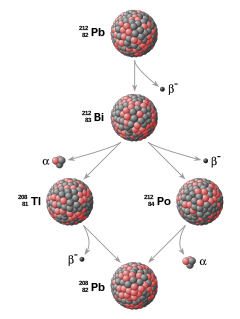
[29] Radioactive elements are used for radiometric dating, the primary method for establishing an absolute time scale in geochronology.
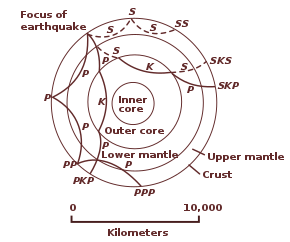
The physical properties of minerals must be understood to infer the composition of the Earth's interior from seismology, the geothermal gradient and other sources of information.
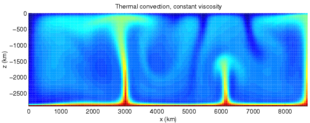
The viscosity of rocks is affected by temperature and pressure, and in turn, determines the rates at which tectonic plates move.
[36] Contrary to popular belief, the earth is not entirely spherical but instead generally exhibits an ellipsoid shape- which is a result of the centrifugal forces the planet generates due to its constant motion.
[37] Earth's shape is constantly changing, and different factors including glacial isostatic rebound (large ice sheets melting causing the Earth's crust to the rebound due to the release of the pressure[38]), geological features such as mountains or ocean trenches, tectonic plate dynamics, and natural disasters can further distort the planet's shape.
For a complete model of the Earth, mineral physics is needed to interpret seismic velocities in terms of composition.
Some parts of this model have been updated by recent findings in mineral physics (see post-perovskite) and supplemented by seismic tomography.
Inside the magnetosphere, there are relatively dense regions of solar wind particles called the Van Allen radiation belts.
Gravity variations detected by GRACE include those caused by changes in ocean currents; runoff and ground water depletion; melting ice sheets and glaciers.
[42] Satellites in space have made it possible to collect data from not only the visible light region, but in other areas of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Measuring the changes in acceleration experienced by spacecraft as they orbit has allowed fine details of the gravity fields of the planets to be mapped.
[54] In 1687 Isaac Newton published his work titled Principia which was pivotal in the development of modern scientific fields such as astronomy and physics.
[55] In it, Newton both laid the foundations for classical mechanics and gravitation, as well as explained different geophysical phenomena such as the precession of the equinox (the orbit of whole star patterns along an ecliptic axis.
[56] Newton's theory of gravity had gained so much success, that it resulted in changing the main objective of physics in that era to unravel natures fundamental forces, and their characterizations in laws.
[55] The first seismometer, an instrument capable of keeping a continuous record of seismic activity, was built by James Forbes in 1844.