Childbirth
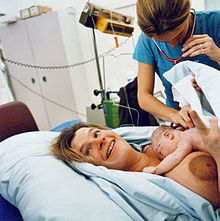
[17] All major health organisations advise that immediately after giving birth, regardless of the delivery method, that the infant be placed on the mother's chest (termed skin-to-skin contact), and to delay any other routine procedures for at least one to two hours or until the baby has had its first breastfeeding.
[39] Oxytocin is further released during labour when the fetus stimulates the cervix and vagina, and it is believed that it plays a major role in the bonding of a mother to her infant and in the establishment of maternal behaviour.
[43] Cervical ripening is the physical and chemical changes in the cervix to prepare it for the stretching that will take place as the fetus moves out of the uterus and into the birth canal.
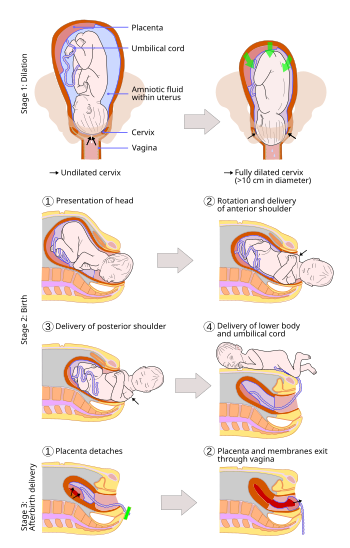
[16] The fourth stage of labour involves recovery, the uterus beginning to contract to pre-pregnancy state, delayed clamping of the umbilical cord, and monitoring of the neonatal tone and vitals.
[17] All major health organisations advise that immediately following a live birth, regardless of the delivery method, that the infant be placed on the mother's chest, termed skin-to-skin contact, and delaying routine procedures for at least one to two hours or until the baby has had its first breastfeeding.
Once the sac ruptures the baby is at risk for infection and the mother's medical team will assess the need to induce labour if it has not started within the time they believe to be safe for the infant.
The average time from delivery of the baby until complete expulsion of the placenta is estimated to be 10–12 minutes dependent on whether active or expectant management is employed.
However, delaying cord cutting in healthy full-term infants results in early haemoglobin concentration and higher birthweight and increased iron reserves up to six months after birth with no change in the rate of postpartum bleeding.
[71][72] The mother has regular assessments for uterine contraction and fundal height,[73] vaginal bleeding, heart rate and blood pressure, and temperature, for the first 24 hours after birth.
Vaginal discharge, termed "lochia", can be expected to continue for several weeks; initially bright red, it gradually becomes pink, changing to brown, and finally to yellow or white.
[81][20] La Leche League advises women to have a delivery team which includes a support person who will advocate to assure that: It has long been known that a mother's level of the hormone oxytocin elevates when she interacts with her infant.
To keep it from dropping any lower, in 1996 Congress passed the Newborns' and Mothers' Health Protection Act that requires insurers to cover at least 48 hours for uncomplicated delivery.
[88][89] Personal expectations, the amount of support from caregivers, quality of the caregiver-patient relationship, and involvement in decision-making are more important in the mother's overall satisfaction with the birthing experience than are other influencing factors such as age, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, preparation, physical environment, pain, immobility, or medical interventions.
[95] At one time shaving of the area around the vagina, was common practice due to the belief that hair removal reduced the risk of infection, made an episiotomy (a surgical cut to enlarge the vaginal entrance) easier, and helped with instrumental deliveries.
For women undergoing operative vaginal delivery with vacuum extraction or forceps, there is strong evidence that prophylactic antibiotics help to reduce the risk of infection.
[105] Most women like to have someone to support them during labour and birth; such as a midwife, nurse, or doula; or a lay person such as the father of the baby, a family member, or a close friend.
[113] Epidural analgesia has no statistically significant impact on the risk of caesarean section, and does not appear to have an immediate effect on neonatal status as determined by Apgar scores.
[114] The World Health Organization recommends its use either alone or with amniotomy (rupture of the amniotic membrane) but advises that it must be used only after it has been correctly confirmed that labour is not proceeding properly if harm is to be avoided.
[118] The World Health Organization (WHO) advises that for healthy women undergoing spontaneous labour continuous cardiotocography is not recommended for assessment of fetal well-being.
The WHO states: "In countries and settings where continuous CTG is used defensively to protect against litigation, all stakeholders should be made aware that this practice is not evidence-based and does not improve birth outcomes.
[139] Postpartum psychosis is a rare psychiatric emergency in which symptoms of high mood and racing thoughts (mania), depression, severe confusion, loss of inhibition, paranoia, hallucinations and delusions set in, beginning suddenly in the first two weeks after childbirth.
[148] Premature birth is the leading cause of death in children under five years of age though many that survive experience disabilities including learning defects and visual and hearing problems.
In 2014 it was estimated that about one in 2000 newborn babies had a group B streptococcuss infection within the first week of life, usually evident as respiratory disease, general sepsis, or meningitis.
[158] Perinatal asphyxia is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm.
The Johns Hopkins Hospital describes the process of receiving the Baby Friendly designation: It involves changing long-standing policies, protocols and behaviors.
[citation needed] Childbirth educators are instructors who aim to teach pregnant women and their partners about the nature of pregnancy, labour signs and stages, techniques for giving birth, breastfeeding and newborn baby care.
[180] Additionally postpartum infections, most often transmitted by the dirty hands and tools of doctors,[86] used to be one of the main causes of maternal mortality until germ theory was accepted in the mid-1800s and adopted thereafter.
[189] Comfort and proximity to extended family and social support systems may be a childbirth priority of many communities in developing countries, such as the Chillihuani in Peru and the Mayan town of San Pedro La Laguna.
[191] In the developed world the placenta may be eaten believing that it reduces postpartum bleeding, increases milk supply, provides micronutrients such as iron, and improves mood and boosts energy.
[86] However, it was not simply a ladies' social bonding event as some historians have portrayed – fear and pain often filled the atmosphere, as death during childbirth was a common occurrence.