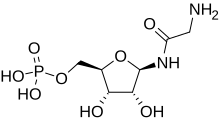
Glycineamide ribonucleotide
Glycineamide ribonucleotide (or GAR) is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA.
[1][2][3] The vitamins thiamine[4] and cobalamin[5] also contain fragments derived from GAR.
[6] GAR is the product of the enzyme phosphoribosylamine—glycine ligase acting on phosphoribosylamine (PRA) to combine it with glycine in a process driven by ATP.
The reaction, EC 6.3.4.13 forms an amide bond:[7] The biosynthesis pathway next adds a formyl group from 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to GAR, catalysed by phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase in reaction EC 2.1.2.2 and producing formylglycinamide ribotide (FGAR):[7]