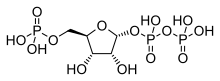
Phosphoribosylamine
Phosphoribosylamine (PRA) is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA.
[1][2][3] The vitamins thiamine[4] and cobalamin[5] also contain fragments derived from PRA.
[6] It is the product of the enzyme amidophosphoribosyltransferase which attaches ammonia from glutamine to phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) at its anomeric carbon:[2] The biosynthesis pathway next combines PRA with glycine in a process driven by ATP giving glycineamide ribonucleotide (GAR).
The enzyme phosphoribosylamine—glycine ligase catalyses the reaction forming an amide bond:[7]