Greenwich Mean Time
[3][a] Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt, noon (12:00:00) GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian[b] and reaches its highest point in the sky there.
To avoid confusion, the name Universal Time was introduced in 1928 to denote GMT as counted from midnight.
[9] The term "GMT" is especially used by institutional bodies within the United Kingdom, such as the BBC World Service, the Royal Navy, and the Met Office; and others particularly in Arab countries, such as the Middle East Broadcasting Centre and Dubai-based OSN.
But this practice, combined with mariners from other nations drawing from Nevil Maskelyne's method of lunar distances based on observations at Greenwich, led to GMT being used worldwide as a standard time independent of location.
For example, our polling booths were opened, say, at 8 13 and closed at 4 13 p.m."[11][12] This was changed later in 1880, when Greenwich Mean Time was legally adopted throughout the island of Great Britain.
[15] The daily rotation of the Earth is irregular (see ΔT) and has a slowing trend; therefore atomic clocks constitute a much more stable timebase.
Universal Time (UT), a term introduced in 1928, initially represented mean time at Greenwich determined in the traditional way to accord with the originally defined universal day; from 1 January 1956 (as decided by the International Astronomical Union in Dublin in 1955, at the initiative of William Markowitz) this "raw" form of UT was re-labelled UT0 and effectively superseded by refined forms UT1 (UT0 equalised for the effects of polar wandering)[16] and UT2 (UT1 further equalised for annual seasonal variations in Earth rotation rate).
Although that instrument still survives in working order, it is no longer in use and now the meridian of origin of the world's longitude and time is not strictly defined in material form but from a statistical solution resulting from observations of all time-determination stations which the BIPM takes into account when co-ordinating the world's time signals.
The long-standing astronomical convention, dating from the work of Ptolemy, was to refer to noon as zero hours (see Julian day).

| Light Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time ( UTC+1 ) | |
| Red | Central European Time ( UTC+1 ) |
| Central European Summer Time ( UTC+2 ) | |
| Yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time ( UTC+2 ) |
| Ochre | Eastern European Time ( UTC+2 ) |
| Eastern European Summer Time ( UTC+3 ) | |
| Green | Moscow Time / Turkey Time ( UTC+3 ) |
| Turquoise | Armenia Time / Azerbaijan Time / Georgia Time / Samara Time ( UTC+4 ) |
▉ ▉ ▉ Dark colours: Summer time observed
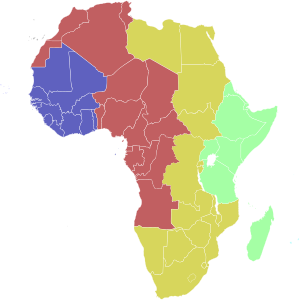
| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time [a] ( UTC−1 ) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Red | ( UTC+1 ) |
| Ochre | ( UTC+2 ) |
| Green | East Africa Time ( UTC+3 ) |
| Turquoise | ( UTC+4 ) |
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.

