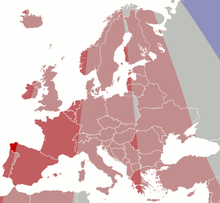
Time in Europe
However, due to geographical and cultural factors, it is not practical to divide the world so evenly, and actual time zones may differ significantly from those based purely on longitude.
However, for example Spain (almost entirely in the Western hemisphere) and France (almost entirely west of 7.5°E, as illustrated in the map below) should theoretically use UTC, as they did before the Second World War.
The European Commission proposed in September 2018 ending the observance of summer time in the EU.
[3] In March 2019, the European Parliament voted in favour of proposing ending seasonal clock changes in 2021.
Of the 27 EU member states (all use daylight saving time in the summer): Of non-EU member states: The overseas territories of Denmark, France, and Netherlands are mostly located outside Europe and use other time zones.

| Light Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC ) |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time ( UTC+1 ) | |
| Red | Central European Time ( UTC+1 ) |
| Central European Summer Time ( UTC+2 ) | |
| Yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time ( UTC+2 ) |
| Ochre | Eastern European Time ( UTC+2 ) |
| Eastern European Summer Time ( UTC+3 ) | |
| Green | Moscow Time / Turkey Time ( UTC+3 ) |
| Turquoise | Armenia Time / Azerbaijan Time / Georgia Time / Samara Time ( UTC+4 ) |
▉ ▉ ▉ Dark colours: Summer time observed