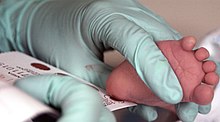
Neonatal heel prick
Other techniques include venous or arterial needle sticks, cord blood sampling, or umbilical line collection.
The test was initially a bacterial inhibition assay, but is gradually being replaced in many areas by newer techniques such as tandem mass spectrometry that can detect a wider variety of congenital diseases.
If a suitably-prepared sample of blood or urine is applied to the seeded agar plate, the growth of the bacteria in the test will be a positive indicator for PKU in the patient.
[4] To prepare the sample for application, a small amount of blood (from a heel puncture, for example) or urine (from a diaper, for example) is applied to a piece of filter paper.
As per the clinical practice guideline issued by the Endocrine Society in 2018, employing LC-MS/MS to measure 17OHP and other adrenal steroid hormones (such as 21-deoxycortisol and androstenedione) is recommended as a supplementary screening approach to enhance the accuracy of positive predictions.
[citation needed] In Ireland, a controversy emerged in 2012 whereby a number of hospitals retained heel prick test cards and thereby a DNA database with over a million samples from 1984, without consent or notification of parents.