Hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome
Seoul virus accounts for about a quarter of HFRS cases, causes a moderate form of the disease, and is found worldwide due to the global distribution of its natural reservoir, the brown rat.
Dobrava-Belgrade virus is the most common cause of HFRS in southern Europe, and varies in disease severity and natural reservoir depending on its genotype.
Removing sources of food for rodents, safely cleaning up after them, and preventing them from entering one's house are all important means of protection.
Other symptoms include headache, lower back pain, impaired vision, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bloody stool.
In severe cases, excess blood clotting throughout the body, called disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), can occur.
An open reading frame in the N gene on the S segment[23] of some hantaviruses also encodes the non-structural protein NS that inhibits interferon production in host cells.
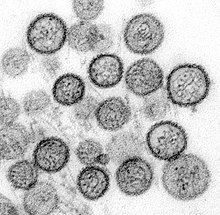
[22] Each surface spike is composed of a tetramer of Gn and Gc (four units each) that has four-fold rotational symmetry, extending about 10 nm out from the envelope.
It can also reportedly spread through human saliva, airborne droplets from coughing and sneezing, and to newborns through breast milk and the placenta.
[2] A 2021 systematic review, however, found human-to-human transmission of the Andes virus to not be strongly supported by evidence but nonetheless possible in limited circumstances, especially between close household contacts such as sexual partners.
[3] The expansion of agricultural land is associated with a decline in predator populations, which enables hantavirus host species to use farm monocultures as nesting and foraging sites.
[33] Seroprevalence, showing past infection to hantavirus, is consistently higher in occupations and areas that have greater exposure to rodents.
[3][14] Infection begins with interaction of the viral glycoproteins Gn and Gc and β-integrin receptors on target cell membranes.
In the spleen, infection of immune cells can cause over-activation of immature lymphocytes elsewhere and facilitate prolonged spread of the virus throughout the body.
Ventilation of rooms before entering, using rubber gloves and disinfectants, and using respirators to avoid inhaling contaminated particles while cleaning up rodent-infested areas reduce risk of hantavirus infections.
[5] Both traditional and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests of blood, saliva, BAL fluids, and tissue samples can be used.
Platelet transfusions can be used to reduce mortality in cases of severe thrombocytopenia and disseminated intravascular coagulation to control bleeding.
If acute kidney injury occurs, then intermittent hemodialysis is used as the first option and continuous renal replacement therapy in critical HFRS cases.
[2][4][7][38] No specific antiviral drugs exist for hantavirus infection, but ribavirin and favipiravir have shown varying efficacy and safety.
[2] Prophylactic use of ribavirin and favipiravir in early infection or post-exposure show some efficacy, and both have shown some anti-hantavirus activity in vivo and in vitro.
Ribavirin is effective in the early treatment of HFRS with some limitations such as toxicity at high doses and the potential to cause hemolytic anemia.
In some instances, ribavirin may cause excess bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia), abnormally slow heart beat (sinus bradycardia), and rashes.
Early production of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) that target the surface glycoproteins is directly associated with increased likelihood of survival.
[3] The Seoul virus is found worldwide due to the global distribution of its hosts, the brown rat, but mainly circulates in China and South Korea and accounts for about a quarter of all HFRS cases.
[41] Rodent species that carry hantaviruses inhabit a diverse range of habitats, including desert-like biomes, equatorial and tropical forests, swamps, savannas, fields, and salt marshes.
[35] High humidity can benefit rodent populations in warm climates, where it may positively impact plant growth and thus food availability.
Heavy rainfall is a risk factor for outbreaks in the following months,[18] but may negatively affect incidence by flooding rodent burrows and nests.
Higher temperatures create unfavorable environments for virus survival, but it can cause rodents to seek shelter from heat in human settings and is beneficial for aerosol production.
[18] Hantavirus hemorrhagic disease was likely first described in the Yellow Emperor's Internal Canon in Imperial China during the Warring States Period of 475-221 BCE.
[31] During the Second World War in 1942, an outbreak of disease with symptoms characteristic of hantavirus infection occurred in Salla, Eastern Lapland, Finland among German and Finnish soldiers.
[31] After the war, in 1976 in South Korea, trapped striped field mice were tested and antigens in their lungs were shown to react to antibodies in sera from survivors of Korean hemorrhagic fever.