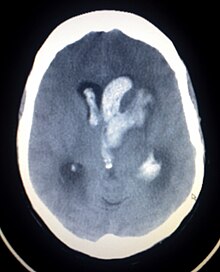
Hemorrhagic infarct
[5] Classified according to one of four origination sites, intracerebral (ICH), subarachnoid, subdural, or epidural.
Treatment can include surgical or endovascular intervention with clips or coils to prevent re-rupture or ventricular drainage or shunting due to hydrocephalus.
Cerebral vasospasm can occur up to two weeks after the subarachnoid hemorrhage, which can cause further ischemia because of the vessel narrowing during the spasm.
Chest X-Ray can demonstrate a "Hampton's Hump" when pulmonary infarction is present, but Cat Scan is more commonly used.
The underlying cause will assist in a treatment plan to include level of care during initial management and the involvement of various specialists as pulmonary infarction can be deadly.
A surgical repair is typically emergent as the ischemia is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates.
The risk of ischemic colitis is directly proportional to age and is more common in the older population but can occur in younger individuals.