Heterosphere
[1] The heterosphere extends from the turbopause to the edge of a planet's atmosphere and lies directly above the homosphere.
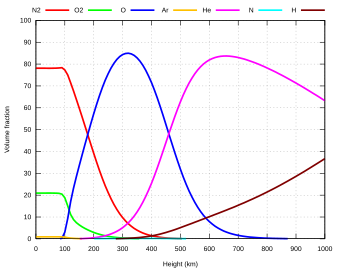
[2] The heterosphere of Earth begins at about 100 km altitude and extends to the outer reaches of its atmosphere.
The major constituents of Earth's heterosphere are nitrogen, oxygen, helium, and hydrogen.
In the higher levels of the heterosphere, above about 1,000 km, helium and hydrogen are the dominant species present.
[2] Due to the diffused nature of the heterosphere's gases, its density at any given height is not entirely dependent on the temperature.