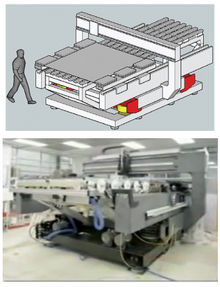
High performance positioning system
Position is typically defined in six degrees of freedom, including linear, in an x,y,z cartesian coordinate system, and angular orientation of yaw, pitch, roll.
It is designed to quickly stop its motion and accurately place the moving object at its desired final position and orientation with minimal jittering.
At their highest performance HPPS may use granite base for thermal stability and flat surfaces, air bearings for jitter free motion, brushless linear motors for non contact, frictionless actuation, high force and low inertia, and laser interferometer for sub micron position feedback.
As a result, in 1996 Siemens integrated its CNC with Anorad linear motors to drive a 20 m' long Maskant machine at Boeing for chemical milling of aircraft wings.
[3] And in 1998, Rockwell Automation acquired Anorad to compete with Siemens and Fanuc in providing a complete linear motor solutions to drive high velocity machine tools in Automotive transfer lines.
[5] System specification (technical standard) is an official interface between the application requirements (problem), as described by the user (customer) and the design (solution) as optimized by the developer (supplier).