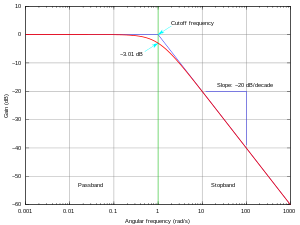
Frequency response
Systems with a specific frequency response can be designed using analog and digital filters.
[4] Nonlinear frequency response methods may reveal effects such as resonance, intermodulation, and energy transfer.
In the audible range frequency response is usually referred to in connection with electronic amplifiers, microphones and loudspeakers.
Infrasonic frequency response measurements include earthquakes and electroencephalography (brain waves).
Similarly, if a system is demonstrated to have a poor frequency response, a digital or analog filter can be applied to the signals prior to their reproduction to compensate for these deficiencies.
The form of a frequency response curve is very important for anti-jamming protection of radars, communications and other systems.
Frequency response analysis can also be applied to biological domains, such as the detection of hormesis in repeated behaviors with opponent process dynamics,[7] or in the optimization of drug treatment regimens.