History of Punjab
Soanian assemblages generally comprise varieties of choppers, discoids, scrapers, cores, and numerous flake type tools, all occurring in varying typo-technological frequencies at different sites.
[5] However, the presence of Gandhāra, referred to as Gandāra in Old Persian, among the list of Achaemenid provinces in Darius's Behistun Inscription confirms that his empire had inherited this region from conquests carried out earlier by Cyrus.
[50][53] The battle is historically significant because it resulted in the syncretism of ancient Greek political and cultural influences to the Indian subcontinent, yielding works such as Greco-Buddhist art, which continued to have an impact for the ensuing centuries.
Under Chanakya's tutelage, Chandragupta received a comprehensive education at Taxila, encompassing various arts of the time, including military training, for a duration spanning 7–8 years.
This engagement is corroborated by Polybius, who records an instance where Antiochus III the Great descended into India to renew his ties with King Subhagasena in 206 BCE, subsequently receiving a substantial gift of 150 elephants from the monarch.
[73][74] Other potential centers are only hinted at; for instance, Ptolemy's Geographia and the nomenclature of later kings suggest that a certain Theophila in the south of the Indo-Greek sphere of influence may also have been a satrapal or royal seat at one time.
The Indo-Greeks ultimately disappeared as a political entity around 10 AD following the invasions of the Indo-Scythians, although pockets of Greek populations probably remained for several centuries longer under the subsequent rule of the Indo-Parthians and Kushans.
This epigraphic source further articulates that Vijayamitra, a descendant of Viyakamitra, approximately half a century after the initial inscription, is credited with its restoration following inflicted damage.
[83] Some Aprachas are documented on the Silver Reliquary discovered at Sirkap, near Taxila, designating the title "Stratega," denoting a position equivalent to Senapati, such as that of Indravarma who was a general during the reign of the Apracharaja Vijayamitra.
Indravarmas son Aspavarma is situated between 20 and 50 CE, during which numismatic evidence overlaps him with the Indo-Scythian ruler Azes II and Gondophares of the Indo-Parthians whilst also describing him as 'Stratega' or general of the Aprachas.
In accordance with a Buddhist Avadana, Aspavarma and a Saka noble, Jhadamitra, engaged in discussions concerning the establishment of accommodation for monks during the rainy seasons, displaying that he was a patron of Buddhism.
[92] It was noted by Philostratus and Apollonius of Tyana upon their visit with Phraotes in 46 AD, that during this time the Gandharans living between the Kabul River and Taxila had coinage of Orichalcum and Black brass, and their houses appearing as single-story structures from the outside, but upon entering, underground rooms were also present.
With fervent support from the populace, Phraotes led a triumphant entry into the residence of the usurpers, whilst the citizens brandished torches, swords, and bows in a display of unified resistance.
This victory appears to have been commemorated in the Hund Slab Inscription (HSI):[119][page needed] At the beginning of the 8th century, Arab armies of the Umayyad Caliphate penetrated into South Asia.
[122] Jayapala's son and grandson, Anandapala and Trilochanapala respectively, resisted Mahmud for another quarter of a century and later by Bhimapala and local Ghakkhar chieftains until Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad's victory in Second battle of Tarain in 1192.
[134] The Tughlaq dynasty's reign formally started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq after defeating Khusrau Khan at the Battle of Lahrawat.
During Ghazi Maliks reign, in 1321 he sent his eldest son Jauna Khan, later known as Muhammad bin Tughlaq, to Deogir to plunder the Hindu kingdoms of Arangal and Tilang (now part of Telangana).
[136] This time Jauna Khan succeeded and Arangal fell, it was renamed to Sultanpur, and all plundered wealth, state treasury and captives were transferred from the captured kingdom to the Delhi Sultanate.The Muslim aristocracy in Lukhnauti (Bengal) invited Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq to extend his coup and expand eastwards into Bengal by attacking Shamsuddin Firoz Shah, which he did over 1324–1325 AD,[135] after placing Delhi under control of his son Ulugh Khan, and then leading his army to Lukhnauti.
After his father's death in 1325 CE, Muhammed Bin Tughlaq assumed power and his rule saw the empire expand to most of the Indian subcontinent, its peak in terms of geographical reach.
[160] The last ruler of the Sayyids, Ala-ud-Din, voluntarily abdicated the throne of the Delhi Sultanate in favour of Bahlul Khan Lodi on 19 April 1451, and left for Badaun, where he died in 1478.
[165] Sultan Husayn I being unable to hold his trans-Indus possessions, assigned the region around Dera Ismail Khan to Sardar Malik Sohrab Dodai Baloch in 1469 or 1471 and appointed him as "Jagir".
[166] The city was invaded during the reign of Sultan Husseyn II by ruler Shah Husayn of the Arghun dynasty, probably at Babur's insistence,[165] who was either ethnic Mongol,[167] or of Turkic or Turco-Mongol extraction.
[168] Multan fell in 1528 after an extended siege and Shah Husayn appointed his son Mirza Askari as governor of the city, assisted by Langar Khan, one of the powerful amirs of Sultan Mahmud Langah I.
Jahangir ordered the execution of Guru Arjan Dev, whilst in Mughal custody, for supporting his son Khusrau Mirza's rival claim to the throne.
The succeeding son of Jahangir, Shah Jahan, took offence at Guru Hargobind's declaration and after a series of assaults on Amritsar, forced the Sikhs to retreat to the Sivalik Hills.
In order to send a message, and prevent such occurrences from recurring, Ahmad Shah destroyed the Golden Temple in Amritsar and filled the Sarovar (Holy water pool) with cow carcasses.
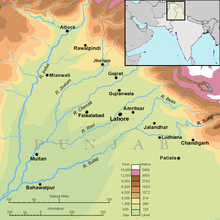
Economically it transformed the Punjab into the richest farming area of India, socially it sustained the power of large landowners and politically it encouraged cross-communal co-operation amongst land owning groups.
[202] Unable to placate their traditional support base with benefits from the colonial administration, they suffered a loss of authority which led to their disastrous performance at the 1946 Punjab Provincial Assembly election and a breakdown in inter-communal cooperation at a political level.
This rapid demographic shift was primarily due to wide scale migration but also caused by large-scale religious cleansing riots which were witnessed across the region at the time.
During Operation Blue Star, Gandhi further called in Indian troops to extinguish the few militants who had taken shelter in the Golden Temple, killing thousands of civilians in the crossfire.