List of rulers of Bengal
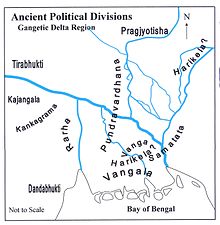
In ancient times, Bengal consisted of the kingdoms of Pundra, Suhma, Vanga, Samatata and Harikela.
In the 4th century BCE, during the reign of the Nanda Empire, the powerful rulers of Gangaridai sent their forces consisting of war elephants which led to the withdrawal of Alexander the Great from the Indian subcontinent.
The Pala period is considered as one of golden eras of Bengali history as it brought stability and prosperity to Bengal after centuries of Civil War, created outstanding works of art and architecture, proto-Bengali language developed under them including its first literary work, the Charyapada and so on.
[7][8] The Bengal Sultanate, a major trading nation in the world,[9] was founded in 1342 by Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, after he united Satgaon, Lakhnauti and Sonargaon.
The Hussain Shahi dynasty founded by Alauddin Husain Shah, reached its greatest territorial extent which saw the extension of the sultanate from modern Bihar and Odisha in the west, to Kamaraupa and the port of Chittagong in the east, witnessing the arrival of the earliest Portuguese merchants.
[14] Known Anga rulers include: Vanga was an ancient kingdom and geopolitical division on the Ganges delta.
There were 52 Janaka (kings) ruled Videha dynasty of Mithila-[20] During this period of fall of Videha dynasty, the famous republic of Licchavi was rising in Vaishali and Mithila region came under control of Licchavi clan of Vajji confederacy in around eighth century BCE.
Some of these writers state that Alexander the Great withdrew from the Indian subcontinent because of the strong war elephant force of the Gangaridai.
A number of modern scholars locate Gangaridai in the Ganges Delta of the Bengal region, although alternative theories also exist.
[24][25] The Bhadra dynasty was a Bengali Hindu royal house of Brahmin origin, their rule flourished during the first half of the 7th century, though little is known about their history.
The Khalji dynasty of Bengal (c.1204–27) were initially representatives of the Ghurid Empire, later becoming independent, although at times being subordinate to the Delhi Sultanate.
The advent of the British East India Company with its "exploitation and oppression" alongside zamindari subjugation, made life of the peasants and farmers difficult and despondent.
With the granting of rent exemption to the peasants, he managed to govern the economy in an appropriate manner, leading to the reduction of the prices of essential commodities.
Following the Regulating Act 1773, the Governor of Bengal was officially called Governor-General of Fort William.
In 1793, the British East India Company abolished Nizamat, i.e. local rule by Mughal emperor- appointed Nawabs and annexed Bengal.