Hurricane Harvey
[4] In a four-day period, many areas received more than 40 inches (1,000 mm) of rain as the system slowly meandered over eastern Texas and adjacent waters, causing unprecedented flooding.
Upon entering the Caribbean, Harvey began to weaken due to moderate wind shear, and degenerated into a tropical wave north of Colombia, late on August 19.
Rapid weakening then ensued, and Harvey had downgraded to a tropical storm as it stalled near the coastline, dropping torrential and unprecedented amounts of rainfall over Texas.
[5] Maintaining its brisk westward motion, the system strengthened slightly and became a tropical storm later that day, at which time it was assigned the name Harvey.
[6] Though it lacked an organized surface low, the remnants of Harvey continued to produce significant convection as it traversed the Caribbean Sea and Yucatán Peninsula.
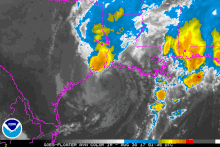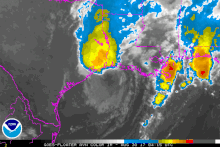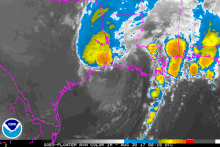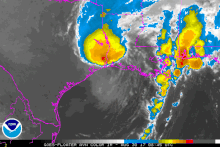
[7] Initial reorganization was slow; however, within a highly favorable environment, the system soon underwent rapid intensification as an eye developed and its central pressure quickly fell.
[9] Around 03:00 UTC on August 26, the hurricane made landfall at peak intensity on San Jose Island, just east of Rockport, with winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) and an atmospheric pressure of 937 mbar (27.7 inHg).
Deep convection persisted north of the cyclone's center near the Houston metropolitan area along a stationary front, resulting in several days of record-breaking rain.
Associated convection with Harvey became focused north of the center and along a warm front on September 1 as it moved further inland, indicating that the system transitioned into a post-tropical cyclone by 06:00 UTC that day.
[18] In Honduras, a green alert was issued for the Atlántida, Islas de la Bahía, Colón, Cortés, Gracias a Dios, Olancho, and Yoro departments.
[19] As the remnants of Harvey approached Mexico, the Civil Protection Secretary of the state of Campeche issued a blue alert, indicating minimal danger.
[20] When Harvey redeveloped at 15:00 UTC on August 23, the Government of Mexico issued a tropical storm watch in Tamaulipas from Boca De Catan to the mouth of the Rio Grande.
[16] As the hurricane neared landfall on August 24, an extreme wind warning—indicating an immediate threat of 115–145 mph (185–235 km/h) winds—was issued for areas expected to be impacted by the eyewall; this included parts of Aransas, Calhoun, Nueces, Refugio, and San Patricio counties.
In New Orleans, there were concerns about whether or not the city's drainage system could handle a heavy rainfall event, with only 105 of the 120 water pumps being operational and some power turbines being out of service.
In the former, high winds in the capital city of Paramaribo caused roof damage to the Presidential Palace and two homes, while the Torarica Hotel and Casino suffered structural impact.
[41] In the city of Lake Charles, flood waters reached 4 ft (1.2 m) in height in some areas, with homes inundated and hundreds of people forced to evacuate in one neighborhood alone.
[44][45] In Alabama, an unusually large, long-tracked EF2 tornado in the vicinity of Reform and Palmetto damaged two homes and destroyed a barn along SR 17, while four people were hospitalized for their injuries.
High wind knocked out power in Fuquay-Varina, Sanford, and Holly Springs, and large hail hit parts of Wake, Harnett, and Johnston counties.
[60] On August 30, the CEO of Arkema warned one of its chemical plants in Crosby, Texas, could explode or be subject to intense fire due to the loss of "critical refrigeration" of materials.
[67] In addition, the Houston Astros were forced to move their August 29–31 series with the Texas Rangers from Minute Maid Park in Houston to Tropicana Field in St. Petersburg, Florida;[68] ironically, just two weeks later, Hurricane Irma would force the stadium's regular tenants, the Tampa Bay Rays, to move three home games to Citi Field in New York City.
[72] The annual Texas Kickoff game that was to feature BYU and LSU to kick off the 2017 college football season was moved to the Mercedes-Benz Superdome in New Orleans.
[77][78] Athletic events were rescheduled as far away as Kentucky, where the storm's remnants were expected to cause heavy rains on September 1, interfering with Friday night high school football.
[83] Texas Governor Greg Abbott deployed the state's entire National Guard for search and rescue, recovery, and clean up operations due to the devastating damage caused by the storm and resulting floods.
[37] A 36-year-old inmate sentenced to death for a 2003 murder was granted a temporary reprieve as a result of Harvey, as his legal team was based in Harris County, an area heavily affected by the hurricane.
[107] Economists Michael Hicks and Mark Burton at Ball State University estimated damage in the Houston metropolitan area alone at $198.63 billion.
[119][better source needed][120] Business aviation played a part in the rescue efforts, providing support during the storm as well as relief flights bringing in suppliers in the immediate aftermath.
The main waterways, the San Jacinto River and the Buffalo Bayou, meander slowly, laden with mud, and have little capacity for carrying storm water.
[150][151][152] The National Climate Assessment states:“The recent increases in activity are linked, in part, to higher sea surface temperatures in the region that Atlantic hurricanes form in and move through.
Numerous factors have been shown to influence these local sea surface temperatures, including natural variability, human-induced emissions of heat-trapping gases, and particulate pollution.
[138] Harvey's stalled position was due to weak prevailing winds linked to a greatly expanded subtropical high pressure system over much of the US at the time, which had pushed the jet stream to the north.

Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown