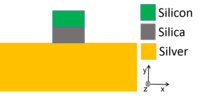Hybrid plasmonic waveguide
It is formed by separating a medium of high refractive index (usually silicon) from a metal surface (usually gold or silver) by a small gap.
[2] The aim of designing the hybrid plasmonic waveguide was to combine these two different wave guiding schemes and achieve high light confinement without suffering large loss.
Many other types of hybrid plasmonic waveguides have been proposed since then to improve light confinement ability or to reduce fabrication complexity.
The most commonly used hybrid plasmonic waveguide consists of a silicon nanowire placed very near a metal surface and separated by a low index region.
Some notable examples of such applications are compact lasers,[8] electro optic modulators,[9] biosensors,[10][11] polarization control devices,[12] and thermo-optic switches.