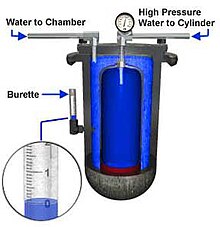
Hydrostatic test
Hydrostatic tests are conducted under the constraints of either the industry's or the customer's specifications, or may be required by law.
The vessel is filled with a nearly incompressible liquid – usually water or oil – pressurised to test pressure, and examined for leaks or permanent changes in shape.
This factor of safety is typically 166.66%, 143% or 150% of the designed working pressure, depending on the regulations that apply.
[citation needed] Portable fire extinguishers are safety tools that are required in most public buildings.
Over time the conditions in which they are housed, and the manner in which they are handled affect the structural integrity of the extinguisher.
Hydrotesting of pipes, pipelines and vessels is performed to expose defective materials that have missed prior detection, ensure that any remaining defects are insignificant enough to allow operation at design pressures, expose possible leaks and serve as a final validation of the integrity of the constructed system.
Since many long distance transmission pipelines are designed to have a steel hoop stress of 80% of specified minimum yield strength (SMYS) at Maximum allowable operating pressure MAOP, this means that the steel is stressed to SMYS and above during the testing, and test sections must be selected to ensure that excessive plastic deformation does not occur.
BS PD 8010-2 requires testing to 150% of the design pressure – which should not be less than the MAOP plus surge and other incidental effects that will occur during normal operation.
Australian standard AS2885.5 "Pipelines – Gas and liquid petroleum: Part 5: Field pressure testing" gives an excellent explanation of the factors involved.
[2] [clarification needed] Gas cylinders which fail are normally destroyed as part of the testing protocol to avoid the dangers inherent in them being subsequently used.
[3] These common US standard gas cylinders have the following requirements:[4] Typically organizations such as DOT PHMSA, ISO, ASTM and ASME specify the guidelines for the different types of pressure vessels.
Adhering to prescribed procedures defined in relevant technical standards appropriate to the specific application and jurisdiction will usually reduce these risks to an acceptable level.