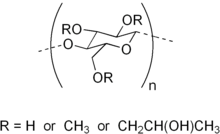
Hypromellose
Hypromellose (INN), short for hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), is a semisynthetic, inert, viscoelastic polymer used in eye drops, as well as an excipient and controlled-delivery component in oral medicaments, found in a variety of commercial products.
[1][2] HPMC has a cellulose backbone with substituents that enhance its water solubility and stability, making it suitable for various applications.
There are many fields of application for hypromellose, including:[6][7] Agricultural Research Service scientists are investigating using the plant-derived HPMC as a substitute for gluten in making all-oat and other grain breads.
HPMC is used primarily in construction materials like tile adhesives and renders[9] where it is used as a rheology modifier, as a water retention agent and retarder, and to improve the workability and application performance of gypsum mixtures.
[10] Functionally HPMC is very similar to HEMC (hydroxy ethyl methyl cellulose) Trade names include Methocel and Walocel.
[13] On a molecular level, this polymer contains beta-linked D-glucose units that remain metabolically intact for days to weeks.
Thus, moisture must be tested and weight corrected to ensure adequate amount of dry active material are apportioned for usage.