Hyperbolic motion (relativity)
Hyperbolic motion is the motion of an object with constant proper acceleration in special relativity.
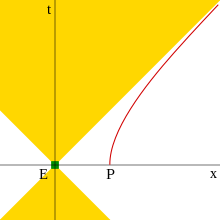
It is called hyperbolic motion because the equation describing the path of the object through spacetime is a hyperbola, as can be seen when graphed on a Minkowski diagram whose coordinates represent a suitable inertial (non-accelerated) frame.
This motion has several interesting features, among them that it is possible to outrun a photon if given a sufficient head start, as may be concluded from the diagram.
[1] Hermann Minkowski (1908) showed the relation between a point on a worldline and the magnitude of four-acceleration and a "curvature hyperbola" (German: Krümmungshyperbel).
[2] In the context of Born rigidity, Max Born (1909) subsequently coined the term "hyperbolic motion" (German: Hyperbelbewegung) for the case of constant magnitude of four-acceleration, then provided a detailed description for charged particles in hyperbolic motion, and introduced the corresponding "hyperbolically accelerated reference system" (German: hyperbolisch beschleunigtes Bezugsystem).
[3] Born's formulas were simplified and extended by Arnold Sommerfeld (1910).
[4] For early reviews see the textbooks by Max von Laue (1911, 1921)[5] or Wolfgang Pauli (1921).
[6] See also Galeriu (2015)[7] or Gourgoulhon (2013),[8] and Acceleration (special relativity)#History.
of a particle is defined as the acceleration that a particle "feels" as it accelerates from one inertial reference frame to another.
If the proper acceleration is directed parallel to the line of motion, it is related to the ordinary three-acceleration in special relativity
is the instantaneous speed of the particle,
Solving for the equation of motion gives the desired formulas, which can be expressed in terms of coordinate time
For simplification, all initial values for time, location, and velocity can be set to 0, thus:[5][6][9][10][11] This gives
, which is a hyperbola in time T and the spatial location variable
In this case, the accelerated object is located at
If instead there are initial values different from zero, the formulas for hyperbolic motion assume the form:[12][13][14] The worldline for hyperbolic motion (which from now on will be written as a function of proper time) can be simplified in several ways.
For instance, the expression can be subjected to a spatial shift of amount
,[14] the equations for hyperbolic motion reduce to[4][16] with the hyperbola
Born (1909),[3] Sommerfeld (1910),[4] von Laue (1911),[5] Pauli (1921)[6] also formulated the equations for the electromagnetic field of charged particles in hyperbolic motion.
[7] This was extended by Hermann Bondi & Thomas Gold (1955)[17] and Fulton & Rohrlich (1960)[18][19] This is related to the controversially[20][21] discussed question, whether charges in perpetual hyperbolic motion do radiate or not, and whether this is consistent with the equivalence principle – even though it is about an ideal situation, because perpetual hyperbolic motion is not possible.
While early authors such as Born (1909) or Pauli (1921) argued that no radiation arises, later authors such as Bondi & Gold[17] and Fulton & Rohrlich[18][19] showed that radiation does indeed arise.
In equation (2) for hyperbolic motion, the expression
However, as pointed out by Sommerfeld,[16] one can define
This means, that the equations become transformations indicating the simultaneous rest shape of an accelerated body with hyperbolic coordinates
as seen by a comoving observer By means of this transformation, the proper time becomes the time of the hyperbolically accelerated frame.
Using these coordinates, it turns out that observers in hyperbolic motion possess an apparent event horizon, beyond which no signal can reach them.
A lesser known method for defining a reference frame in hyperbolic motion is the employment of the special conformal transformation, consisting of an inversion, a translation, and another inversion.
[22] It is commonly interpreted as a gauge transformation in Minkowski space, though some authors alternatively use it as an acceleration transformation (see Kastrup for a critical historical survey).
[23] It has the form Using only one spatial dimension by
the time becomes singular, to which Fulton & Rohrlich & Witten[24] remark that one has to stay away from this limit, while Kastrup[23] (who is very critical of the acceleration interpretation) remarks that this is one of the strange results of this interpretation.