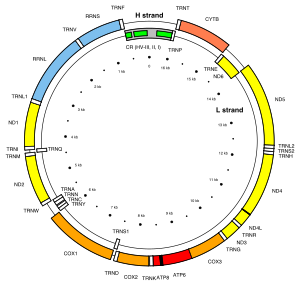
Hypervariable region
A hypervariable region (HVR) is a location within a sequence where polymorphisms frequently occur.
[2][3] In some bony fishes, for example certain Protacanthopterygii and Gadidae, the mitochondrial control region evolves remarkably slowly.
In the Ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis), an East Asian protacanthopterygian, control region mutation rate is not markedly lowered, but sequence differences between subspecies are far lower in the control region than elsewhere.
[4] The 16S ribosomal RNA in prokaryotes have nine hypervariable regions where mutation rates are higher than neighboring parts, numbered V1 to V9.
Their repeated nature allows a unique form of mutation: the number of copies can increase or decrease when strand slippage occurs during DNA replication.