Hypostatic model of personality
The term hypostasis can cover a wide range of personality-related entities usually known as type, stage, trait, system, approach.
[9] In linguistics, Leonard Bloomfield introduced the concept of hypostasis[10] to describe the personification of an object or state in sentences as I'm tired of your buts and ifs.
[18] The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory uses ten clinical scales measuring dimensions whose development and correlations in an individual determine her pathological tendencies.
[21] Differentiation between various mental states and behavior patterns on the basis of their relation with brain and social environment became commonplace in contemporary psychology and sociology.
[25] C. Robert Cloninger defines three independent dimensions of personality, which are related to heritable variation in patterns of response to specific types of environmental stimuli; variation in each dimension is strongly correlated with activity in a specific central monoaminergic pathway:[26] On the social-environmental side, role theory[27] defines the role as a set of connected behaviors, rights and obligations as conceptualized by actors in a social situation.
[29] As a core idea of his transactional analysis, Eric Berne asserts that there are at least three "persons" in each of us, calling them our "ego states": the Child (the emotional in us), the Adult (the rational in us), and the Parent (the authoritarian in us).
[45] In addition to this "doing" dimension of personality, there is also a "being made" dimension, including the constitutive axes – each one formed of a mental content (which can be cognitive, verbal, motivational, or pragmatic, depending on the personality aspect), a mental and behavioral activity related to it (which can be cognitive, practical, affective, expressive, regulative, or adaptive), and their brain and environmental correlates, respectively.
This model provides a picture of the emergent relations between personality structuring, mental functioning (behavior), environment, and biology.
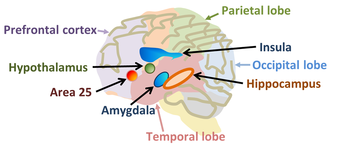
[47] Research using functional magnetic resonance imaging of the brain suggests that cognitive and affective-expressive forms of communication and self-reflection have distinct neural bases.
These experimental results suggest that reading and recognition of face expressions are stimulus-dependent and perhaps hierarchical behaviors, hence recruiting distinct regions of the medial prefrontal cortex.
[52] Research suggested that the fundamental mechanism at the basis of the experiential understanding of others’ actions is the activation of the mirror neuron system.
[54] Evidence suggests that there are at least two large-scale neural networks: frontoparietal mirror-neuron areas related to perceptual-motor interactions with others, and cortical midline structures that engage in processing information about the self and others in cognitive and evaluative terms.
[66] For example, while homosexual behavior does not have biological (reproductive) effect, it has social adaptive value in cultures that permit it or, as in ancient Greece, require it.
[66] In critical situations, biological and social fields of adaptation converge, forming an integrated, bio-social adaptation system:[67] confronted with new and spreading disease and risk factors, modern medicine made people live longer, healthier, more productive lives, and that, in turn, set the ground for further progress of civilization.
Nobel laureate Ralph M. Steinman prolonged his life with the help of his own scientific discoveries, and this allowed him to continue research in cancer immunotherapy.
[68] Preliminary experiments needing extensive verification[67] have suggested that in well-rested subjects, engaging in "biological" behavior (eating, sex) does not lead to lowering of mental energy levels, as measured with a self-assessment scale, and engaging in "psychosocial" behavior (cognitive tasks) does not lead to lowering of physical energy levels (measured with a similar scale).
However, in subjects with exhaustion both results were positive (feeding-related and sexual activities lowered both physical and mental energy levels, and engaging in cognitive tasks did the same).
During adulthood, the person is usually capable of creation and self-determination, and development can follow paths such as these:[72] The unusual, the unnatural, and the counter-cultural in the area of mental life have been – in all ages – "subject of astonishment and reflection for individual reason, object of exclusion and confinement for social action", being met with "reserve or even repulsion by the public and with interest and even fascination by thinkers".
[73] In all cultures, aspects of internal disorganization and adaptive inefficiency of the person have generally been considered abnormal, whether they were referenced as "demonic possession", "madness", "mental illness", or "deviance" by different societies and theories.
[75] People tend to neglect stimuli with low cognitive or affective significance to them, as well as forget excessively intense emotions and information that is too difficult for them to understand.
It is also called the method of hypostatic definition, because of "defining" a person through her genus (in this case the nearest neighbor) by outlining her differentia.
[83] The steps of the technique are:[83] In this kind of humanistic "psychological engineering",[84] setting the goals for personality change is completely non-normative and non-judgemental.
There is nothing wrong that must be remedied, no disease to cure, but an end state to be reached, like in the following goal formulations by the subjects and/or their families:[84] The model uses the following methods of assessment and intervention: The psycho-molecular method uses specific tasks in order to influence specific neurotransmitter systems.
[84] Through the control of the environment which is selectively enriched or deprived, some of the subject's brain areas can be stimulated or inhibited systematically, leading to changes in the seric levels of the metabolites of certain neurotransmitters, associated with clinical improvement in burnout individuals.
Stimulating techniques involve the presence of environmental materials that allow a single type of activity (cognitive, practical, affective, or expressive).
[104] We instruct the patient to put himself into a state of quiet, unreflecting self-observation, and to report to us whatever internal observations he is able to make [...] not to exclude any of them, whether on the ground that it is too disagreeable or too indiscreet to say, or that it is too unimportant or irrelevant, or that it is nonsensical and need not be said.Being genuine also involves the willingness to be and to express, in my words and my behavior, the various feelings and attitudes which exist in me.[...]
The therapist asks the client about what she thinks she could do to counteract those crossed relations, in order to improve communication relationships with those people, and makes suggestions to her, if she has no ideas.
If that is true, the problem is with the student – she tends to express her feelings indirectly, through her actions (feeling-action crossed intrapersonal relation).
If that is not true, and the student was just lazy or incompetent, the problem is with the teacher – he tends to take personally and process emotionally the acts of others (action-feeling crossed interpersonal relation).
[96][97] It alludes to understanding the effects of illicit substances and disease, as well as the underlying change in personality which likely ensues in relation.