Internal globus pallidus
[1] The efferent bundle is constituted first of the ansa and lenticular fasciculus, then crosses the internal capsule within and in parallel to the Edinger's comb system then arrives at the laterosuperior corner of the subthalamic nucleus and constitutes the field H2 of Forel, then H, and suddenly changes its direction to form field H1 that goes to the inferior part of the thalamus.
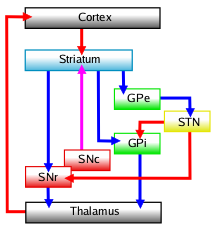
As the GPi is one of the direct output centers of the basal ganglia, this causes disinhibition of the thalamus, increasing overall ease of initiating and maintaining movement.
[5] Dysfunction of the internal globus pallidus has been correlated to Parkinson's disease,[6] Tourette syndrome,[7] and tardive dyskinesia.
[8] The internal globus pallidus is the target of deep brain stimulation (DBS) for these diseases.
[7] The GPi is also considered a "highly effective target for neuromodulation" when using deep brain stimulation on Parkinson's disease patients.