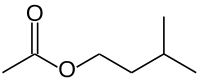
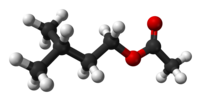
Isoamyl acetate
[5] Isoamyl acetate occurs naturally in many plants, including apple, banana, coffee, grape, guava, lychee, papaya, peach, pomegranate, and tomato.
[6][7] It is also released by fermentation processes, including those used for making beer, sake, cognac, and whisky.
As a solvent and carrier for materials such as nitrocellulose, it was extensively used in the aircraft industry for stiffening and wind-proofing fabric flying surfaces, where it and its derivatives were generally known as 'aircraft dope'.
Now that most aircraft wings are made of metal, such use is mostly limited to historically accurate reproductions and scale models.
Because of its intense, pleasant odor and its low toxicity, isoamyl acetate is used to test the effectiveness of respirators or gas masks.