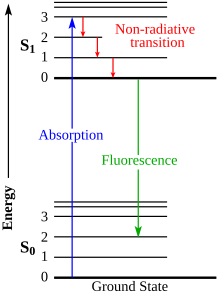
Jablonski diagram
The states are arranged vertically by energy and grouped horizontally by spin multiplicity.
[2] The diagram is named after the Polish physicist Aleksander Jabłoński who first proposed it in 1933.
Likewise, when an excited molecule releases energy, it can do so in the form of a photon.
The changes between these levels are called "transitions" and are plotted on the Jablonski diagram.
[4] A third type is intersystem crossing (ISC); this is a transition to a state with a different spin multiplicity.