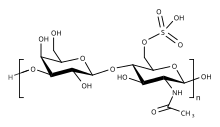
Keratan sulfate
[2] Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.
[4] A third type of KS (KSIII) has also been isolated from brain tissue that is O-linked to specific serine or threonine amino acids via mannose.
Osteoadherin and Fibromodulin linked KS chains are shorter than those found in the cornea, typically 8-9 disaccharide units in length.
[13] Whereas corneal KSI is composed of a number of domains showing variable degrees of sulphation the longest of which may be 8-32 disaccharide units in length.
[8] Fucosylation is also common with alpha-linked fucose present at the carbon 3 position of sulphated GlcNAc, except in the case of tracheal KSII where this feature is absent.