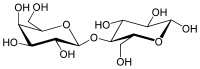
Lactose
[8] Lactose is hydrolysed to glucose and galactose, isomerised in alkaline solution to lactulose, and catalytically hydrogenated to the corresponding polyhydric alcohol, lactitol.
This enzyme cleaves the lactose molecule into its two subunits, the simple sugars glucose and galactose, which can be absorbed.
[17] By descent, more than 70% of western Europeans can digest lactose as adults, compared with less than 30% of people from areas of Africa, eastern and south-eastern Asia and Oceania.
Depending on ingested dose, combination with meals (either solid or liquid), and lactase activity in the intestines, the caloric value of lactose ranges from 2 to 4 kcal/g.
[19] Its mild flavor and easy handling properties have led to its use as a carrier and stabiliser of aromas and pharmaceutical products.
[5] Lactose is not commonly added directly to food, because its low solubility can lead to a gritty mouthfeel.
[24] One of the undesirable properties of lactose utilization is its low solubility, which can result in crystallization, giving a gritty and sandy mouthfeel in the final product.
Usually, in supersaturated solution, sugars tend to crystallize, also forming big agglomerates, depending on the process condition Lactose is not fermented by most yeast during brewing, which may be used to advantage.
Yeast belonging to the genus Kluyveromyces have a unique industrial application, as they are capable of fermenting lactose for ethanol production.
Surplus lactose from the whey by-product of dairy operations is a potential source of alternative energy.
Lactose is added to tablet and capsule drug products as an ingredient because of its physical and functional properties (examples are atorvastatin, levocetirizine or thiamazole among many others).
[28] In 1700, the Venetian pharmacist Lodovico Testi (1640–1707) published a booklet of testimonials to the power of milk sugar (saccharum lactis) to relieve, among other ailments, the symptoms of arthritis.