Land
Earth's land surface is almost entirely covered by regolith, a layer of rock, soil, and minerals that forms the outer part of the crust.
Streams – a major part of Earth's water cycle – shape the landscape, carve rocks, transport sediments, and replenish groundwater.
At high elevations or latitudes, snow is compacted and recrystallized over hundreds or thousands of years to form glaciers, which can be so heavy that they warp the Earth's crust.
In recent decades, scientists and policymakers have emphasized the need to manage land and its biosphere more sustainably, through measures such as restoring degraded soil, preserving biodiversity, protecting endangered species, and addressing climate change.
The equivalent suffix -stan from Indo-Iranian, ultimately derived from the Proto-Indo-Iranian * sthāna-,[10] is also present in many country and location names, such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, and others throughout Central Asia.
The earliest material found in the Solar System is dated to 4.5672±0.0006 bya (billion years ago);[14] therefore, Earth itself must have been formed by accretion around this time.
In theory, a solar nebula partitions a volume out of a molecular cloud by gravitational collapse, which begins to spin and flatten into a circumstellar disc, out of which the planets then grow (in tandem with the star).
Once land became capable of supporting life, biodiversity evolved over hundreds of millions of years, expanding continually except when punctuated by mass extinctions.
The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands.
[47]: 3 Erosion and tectonics, volcanic eruptions, flooding, weathering, glaciation, the growth of coral reefs, and meteorite impacts are among the processes that constantly reshape Earth's surface over geological time.
Densely populated cities are warmer and create urban heat islands that have effects on the precipitation, cloud cover, and temperature of the region.
The shore extends from the low tide line to the highest elevation that can be reached by storm waves, and the coast stretches out inland until the point where ocean-related features are no longer found.
Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of sessile animals (e.g. mussels, starfish, barnacles) and various kinds of seaweeds.
[47]: 99 Both volcanic activity such as the upwelling of magma and extrusion of lava, or erosion of mountains caused from water, glaciers, or aeolian processes, can create plateaus.
Buttes are smaller, with less extrusive and more intrusive igneous rock, while plateaus or highlands are the widest, and mesas are a general-sized plateau with horizontal bedrock strata.
Plains are known to have fertile soils and be important for agriculture due to their flatness supporting grasses suitable for livestock and facilitating the harvest of crops.
The world's ecosystems are impacted in far-reaching ways by the processes carried out in the soil, with effects ranging from ozone depletion and global warming to rainforest destruction and water pollution.
[99] As the planet warms, it has been predicted that soils will add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere due to increased biological activity at higher temperatures, a positive feedback (amplification).
[104] Land provides many ecosystem services, such as mitigating climate change, regulating water supply through drainage basins and river systems, and supporting food production.
[133] A similar model is found in the Homeric account of the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods.
[139] Navigation on land is often facilitated by reference to landmarks – enduring and recognizable natural or artificial features that stand out from their nearby environment and are often visible from long distances.
[142] The second period, occurring over roughly the last 10,000 years, saw increased cross-cultural exchange through trade and exploration, marking a new era of cultural intermingling.
[146] The Dark Ages led trade to collapse in the West, but it continued to flourish among the kingdoms of Africa, the Middle East, India, China, and Southeast Asia.
To address this, a burgeoning banking industry enabled the shift to movable wealth or capital, making it far easier and safer to trade across long distances.
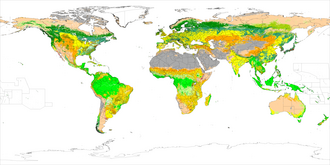
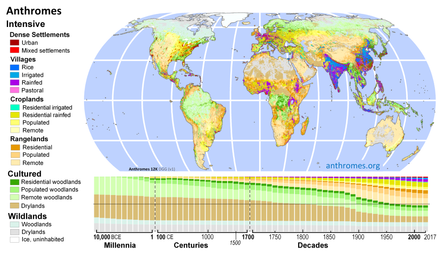
Beginning with the Neolithic Revolution and the spread of agriculture around the world, human land use has significantly altered terrestrial ecosystems, with an essentially global transformation of Earth's landscape by 3000 years ago.
[148]: 30 [149][150] From around 1750, human land use has increased at an accelerating rate due to the Industrial Revolution, which created a greater demand for natural resources and caused rapid population growth.
[159] In the 19th-century United States, a concept of manifest destiny was developed by various groups, asserting that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
[167] Human activity is a major factor in the Holocene extinction,[168] and human-caused climate change is causing rising sea levels and ecosystem loss.
Environmental scientists study land's ecosystems, natural resources, biosphere (fauna and flora), troposphere, and the impact of human activity on these.
[171] This spread of arid areas can be influenced by a variety of human factors, such as deforestation, improper land management, overgrazing,[172] anthropogenic climate change,[173] and overexploitation of soil.