Lanthanum carbide
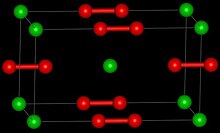
[3] The structure of LaC2 can be described as La3+C22−(e-) where the electron enters the conduction band and antibonding orbitals on the C2 anion, increasing the bond length.
[4] A method for making macroscopic quantities of C60 and the confirmation of the hollow, cagelike structures was published in 1990 by Kratschmer and co-workers.
A 1998 study by Stevenson et al. verified the presence of La@C72 as well as La2@C72, but empty-cage C72 was absent, based on laser desorption mass spectrometry and UV−vis spectroscopy.
[9] A 2008 study by Lu et al. showed that La2C72 do not adhere to the isolated pentagon rule (IPR), but has two pairs of fused pentagons at each pole of the cage and that the two La atoms reside close to the two fused-pentagon pairs.
This result lends additional support to the idea that the carbon cage is stabilized by the La atoms.