Great Lakes
[6][7][8][9] The Great Lakes began to form at the end of the Last Glacial Period around 14,000 years ago, as retreating ice sheets exposed the basins they had carved into the land, which then filled with meltwater.
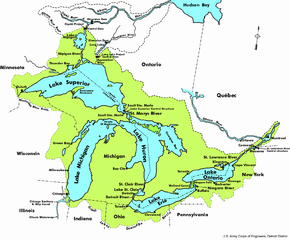
From the interior to the outlet at the Saint Lawrence River, water flows from Superior to Huron and Michigan, southward to Erie, and finally northward to Lake Ontario.
The lakes are divided among the jurisdictions of the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. states of Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York.
[19] The straits are five miles (8 km) wide[14] and 120 feet (37 m) deep; the water levels rise and fall together,[20] and the flow between Michigan and Huron frequently reverses direction.
Population centers on the peninsulas include Grand Rapids, Flint, and Detroit in Michigan along with London, Hamilton, Brantford, and Toronto in Ontario.
The lakes contain about 84% of the surface freshwater of North America;[48] if the water were evenly distributed over the entire continent's land area, it would reach a depth of 5 feet (1.5 meters).
[50] The total surface area of the lakes is approximately 94,250 square miles (244,100 km2)—nearly the same size as the United Kingdom, and larger than the U.S. states of New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Massachusetts, Vermont, and New Hampshire combined.
The Great Lakes have a humid continental climate, Köppen climate classification Dfa (in southern areas) and Dfb (in northern parts)[58] with varying influences from air masses from other regions including dry, cold Arctic systems, mild Pacific air masses from the west, and warm, wet tropical systems from the south and the Gulf of Mexico.
As the slightly warmer, moist air passes over the colder land surface, the moisture often produces concentrated, heavy snowfall that sets up in bands or "streamers".
"[63] By 1801, the New York Legislature found it necessary to pass regulations curtailing obstructions to the natural migrations of Atlantic salmon from Lake Erie into their spawning channels.
In the early 19th century, the government of Upper Canada found it necessary to introduce similar legislation prohibiting the use of weirs and nets at the mouths of Lake Ontario's tributaries.
Periodic mass die-offs result in vast numbers of the fish washing up on shore; estimates by various governments have placed the percentage of Lake Michigan's biomass which was made up of alewives in the early 1960s as high as 90%.
In the late 1960s, the various state and federal governments began stocking several species of salmonids, including the native lake trout as well as non-native chinook and coho salmon; by the 1980s, alewife populations had dropped drastically.
The goby is considered undesirable for several reasons: it preys upon bottom-feeding fish, overruns optimal habitat, spawns multiple times a season, and can survive poor water quality conditions.
More recently an electric fence has been set up across the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal in order to keep several species of invasive Asian carp out of the lakes.
[87] In early August 2019, satellite images depicted a bloom stretching up to 1,300 square kilometres on Lake Erie, with the heaviest concentration near Toledo, Ohio.
[90] The International Joint Commission in 2009 summarized the change: "Since the early 1970s, the level of treatment to reduce pollution from waste water discharges to the Great Lakes has improved considerably.
[citation needed] This describes when older sewerage systems, which combine storm water with sewage into single sewers heading to the treatment plant, are temporarily overwhelmed by heavy rainstorms.
While enormous public investments such as the Deep Tunnel projects in Chicago and Milwaukee have greatly reduced the frequency and volume of these events, they have not been eliminated.
[91] Reports about this issue on the U.S. side highlight five large municipal systems (those of Detroit, Cleveland, Buffalo, Milwaukee and Gary) as being the largest current periodic sources of untreated discharges into the Great Lakes.
The project captured 74,000 pieces of trash using this technology between 2020 and 2021; however, it does not claim to catch up with 22 million pounds (10.0 kt) of plastic that ends up in Great Lakes every year.
[97] Algae such as diatoms, along with other phytoplankton, are photosynthetic primary producers supporting the food web of the Great Lakes,[98] and have been affected by global warming.
[103][104] The peoples of the Great Lakes traded from around 1000 AD, as copper nuggets have been extracted from the region and fashioned into ornaments and weapons in the mounds of Southern Ohio.
The brigantine Le Griffon, which was commissioned by René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, was built at Cayuga Creek, near the southern end of the Niagara River, and became the first known sailing ship to travel the upper Great Lakes on August 7, 1679.
Since general freight these days is transported by railroads and trucks, domestic ships mostly move bulk cargoes, such as iron ore, coal and limestone for the steel industry.
[110] Following a small uproar, the Senate voted to revoke the designation on March 24 (although New York and Vermont universities would continue to receive funds to monitor and study the lake).
A contemporary account by Methodist missionary John Evans describes the fish as resembling a "bright cloud moving rapidly through the water".
The greatest concentration of shipwrecks lies near Thunder Bay (Michigan), beneath Lake Huron, near the point where eastbound and westbound shipping lanes converge.
Major ports on the Great Lakes include Duluth-Superior, Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, Twin Harbors, Hamilton and Thunder Bay.
In 1998, the Canadian company Nova Group won approval from the Province of Ontario to withdraw 158,000,000 U.S. gallons (600,000 m3) of Lake Superior water annually to ship by tanker to Asian countries.