Level Mountain
A wide range of rock types were produced during these stages, namely ankaramites, alkali basalts, trachybasalts, mugearites, hawaiites, phonolites, trachytes and rhyolites.
[9] The lower, but more extensive basal shield volcano rises from an elevation of 900 to 1,400 m (3,000 to 4,600 ft) above the surrounding forested lowlands much like an inverted dishware plate.
[18] Level Mountain is in the Stikine Plateau Ecosection, an area of partially dissected upland characterized by rounded ridges and wide valleys.
[21] Although alpine vegetation of the Stikine Plateau Ecosection can be lush and grass-rich above the tree line, wetlands and muskegs are the dominant ecosystems on Level Mountain.
Mature white spruce and lodgepole pine forests dominate north of Level Mountain where bog birch occurs in river valley bottoms.
Shallow, coarse, textured and steep to strongly sloping soils dominate peaks of the Level Mountain Range and owe their origin to weathering of volcanic rocks.
The gently undulating alpine portions of Level Mountain have been affected by cryoturbation, resulting in patterned ground in which coarse material has been separated from each other as patches or stripes.
[49] Intense glaciation has taken place at Level Mountain in the last 5.33 million years, as shown by the presence of strongly developed glacial grooves reaching elevations greater than 1,675 m (5,495 ft).
[16] Level Mountain is part of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province (NCVP), a broad area of shield volcanoes, lava domes, cinder cones and stratovolcanoes extending from northwestern British Columbia northwards through Yukon into easternmost Alaska.
[53] The dominant rocks comprising these volcanoes are alkali basalts and hawaiites, but nephelinite, basanite and peralkaline[c] phonolite, trachyte and comendite are locally abundant.
This subprovince, confined to the Stikine region of northwestern British Columbia, consists of three other volcanic complexes: Heart Peaks, Hoodoo Mountain and Mount Edziza.
[70] The other planar fracture, Nahlin, is an east-dipping thrust fault extending several hundred kilometres from northern British Columbia into southern Yukon.
[17][50] Several outcrops of alkali basalt south of Kennicott Lake and the Tahltan River are comparable in age to the Level Mountain shield volcano and may represent erosional remnants of this structure.
[17] It is possible that geothermal outputs at Level Mountain had an influence on dynamics of past ice sheets much like the modern Grímsvötn caldera is an important heat source beneath Vatnajökull in Iceland.
[5] Successive eruptions sent lava pouring in all directions from central vents, forming a broad, gently sloping volcano of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's shield.
[16] Alkali basalts and ankaramites were the main lavas produced during this stage of activity which, due to their low silica content, were able to travel great distances away from their source.
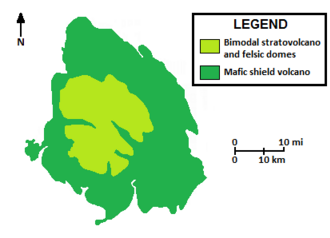
[17] This tremendous variation in the erupted magmas and influence of adjacent vents gave rise to a high and voluminous bimodal stratovolcano located centrally atop the shield.
[17][81] Volcanic rocks of felsic composition, notably peralkaline trachyte and comendite, were the main products comprising this structure, forming more than 80% of its volume.
[17] By the Pliocene epoch, radially directed alpine glaciers had eroded away much of the bimodal stratovolcano, leaving behind a series of U-shaped valleys with intervening ridges that comprise the Level Mountain Range.
[50] Exposed on the south side of Level Mountain near Hatchau Lake is a rock outcrop consisting of boulders cemented together by calcareous sinter.
[91] Radiocarbon dating of terrestrial plant macrofossils 2 to 2.5 centimetres (0.79 to 0.98 inches) above the youngest tephra deposit suggest an early Holocene age for this volcanic material.
This is particularly true around the steep south and west plateau boundaries where relatively clay-rich, incompetent layers of agglomerates and tuffs are present between more competent basaltic lava flows.
Egnell died on June 22, 1900, from an accidental gun shot to his leg by his son, McDonald, five days earlier and was buried at the Liard Post near the mouth of the Dease River.
[6] Along the south side of Level Mountain are a number of other localities, including Hyland Ranch, Saloon, Salmon Creek Indian Reserve No.
[18] This field, consisting of flat-topped summits or benches, was considered to have formed as a result of block faulting or by erosion of a formerly much more extensive surface underlain by horizontally bedded volcanic rocks.
[86] In 1994, Carignnan et al. considered Level Mountain to be underlain by a mantle plume[w] or hotspot[x] due to its proximity to a major continental divide between the Yukon, Arctic and Pacific watersheds.
However, P-wave studies conducted in 1998 by Frederikson et al. did not detect any geophysical anomalies near the mountain to justify the existence of a mantle plume or hotspot.
[16][17] Although the mountain appears level when viewed from a distance, it attains the shape of a large triangle when examined from the top of some of the high hills west of the bend of the Tuya River.
[4] The closest route to this major volcanic complex is a graded road from Dease Lake to Telegraph Creek, which extends within 50 km (31 mi) of the mountain.
[4][17] The Yukon Telegraph Trail, a historic pathway built in the 1890s, is still passable through Hatin Lake and provides an overland route to the shield volcano.