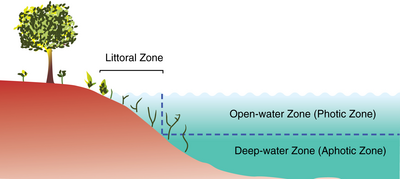
Limnetic zone
The limnetic zone is the open and well-lit area of a freestanding body of fresh water, such as a lake or pond.
[1] The floor under the limnetic zone cannot sustain plant growth due to a lack of sunlight for photosynthesis.
In extremely shallow bodies of water, light may penetrate all the way to floor even in the deepest center parts of the lake.
Oxygen is dissolved when air interacts with water on the surface, and is increased with wave and wind action.
Zooplankton populations often consist of copepods, cladocerans, and rotifers occurring in the open water of lakes.