Fish
The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms.
The earliest fish with dedicated respiratory gills and paired fins, the ostracoderms, had heavy bony plates that served as protective exoskeletons against invertebrate predators.
Commercial and subsistence fishers harvest fish in wild fisheries or farm them in ponds or in breeding cages in the ocean.
Fish are caught for recreation, or raised by fishkeepers as ornaments for private and public exhibition in aquaria and garden ponds.
Fish have had a role in human culture through the ages, serving as deities, religious symbols, and as the subjects of art, books and movies.
[1][2][3][4] About 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion, fishlike animals with a notochord and eyes at the front of the body, such as Haikouichthys, appear in the fossil record.
[16] Fish range in size from the huge 16-metre (52 ft) whale shark[22] to some tiny teleosts only 8-millimetre (0.3 in) long, such as the cyprinid Paedocypris progenetica[23] and the stout infantfish.
[31] The deepest living fish in the ocean so far found is a cusk-eel, Abyssobrotula galatheae, recorded at the bottom of the Puerto Rico Trench at 8,370 m (27,460 ft).
[38] A single undescribed species of Phreatobius has been called a true "land fish" as this worm-like catfish strictly lives among waterlogged leaf litter.
[42] Cleaning behaviors have been observed in a number of fish groups, including an interesting case between two cichlids of the same genus, Etroplus maculatus, the cleaner, and the much larger E.
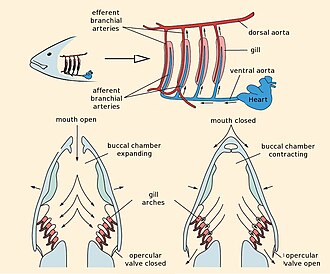
[45] The body of a typical fish is adapted for efficient swimming by alternately contracting paired sets of muscles on either side of the backbone.
Many bony fish have an internal organ called a swim bladder that allows them to adjust their buoyancy by increasing or decreasing the amount of gas it contains.
Some coastal fish like rockskippers and mudskippers choose to leave the water to feed in habitats temporarily exposed to the air.
The hindbrain controls swimming and balance.The single-lobed cerebellum is the biggest part of the brain; it is small in hagfish and lampreys, but very large in mormyrids, processing their electrical sense.
[57] The lateral line system is a network of sensors in the skin which detects gentle currents and vibrations, and senses the motion of nearby fish, whether predators or prey.
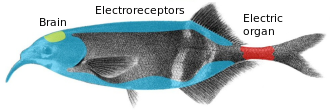
[60] Some fish, such as catfish and sharks, have the ampullae of Lorenzini, electroreceptors that detect weak electric currents on the order of millivolt.
Manta rays and wrasses placed in front of a mirror repeatedly check whether their reflection's behavior mimics their body movement.
The degree of endothermy varies from the billfishes, which warm only their eyes and brain, to the bluefin tuna and the porbeagle shark, which maintain body temperatures more than 20 °C (68 °F) above the ambient water.
[84] Over 97% of fish, including salmon and goldfish, are oviparous, meaning that the eggs are shed into the water and develop outside the mother's body.
The larval period in oviparous fish is usually only some weeks, and larvae rapidly grow and change in structure to become juveniles.
Non-specific defenses include the skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps and inhibits the growth of microorganisms.
Specific defenses respond to particular antigens, such as proteins on the surfaces of pathogenic bacteria, recognised by the adaptive immune system.
It is often more efficient to gather food by working as a group, and individual fish optimise their strategies by choosing to join or leave a shoal.
When a predator has been noticed, prey fish respond defensively, resulting in collective shoal behaviours such as synchronised movements.
[98] The longsnout seahorse, Hippocampus reidi produces two categories of sounds, 'clicks' and 'growls', by rubbing their coronet bone across the grooved section of their neurocranium.
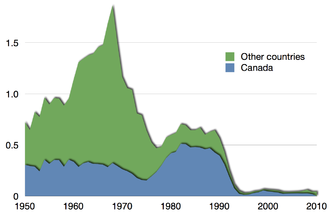
[111] The Food and Agriculture Organization reports that "in 2017, 34 percent of the fish stocks of the world's marine fisheries were classified as overfished".
Harmful species include fish but are not limited to them;[125] the arrival of a comb jelly in the Black Sea damaged the anchovy fishery there.
[126][125] The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 made possible Lessepsian migration, facilitating the arrival of hundreds of Indo-Pacific marine species of fish, algae and invertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea, deeply impacting its overall biodiversity [127] and ecology.
The most common form of recreational fishing employs a rod, reel, line, hooks, and a wide range of baits.
[147] Large fish, particularly sharks, have frequently been the subject of horror movies and thrillers, notably the novel Jaws, made into a film which in turn has been parodied and imitated many times.