List of Solar System objects by size
These lists contain the Sun, the planets, dwarf planets, many of the larger small Solar System bodies (which includes the asteroids), all named natural satellites, and a number of smaller objects of historical or scientific interest, such as comets and near-Earth objects.
Many trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) have been discovered; in many cases their positions in this list are approximate, as there is frequently a large uncertainty in their estimated diameters due to their distance from Earth.
Astronomical bodies relax into rounded shapes (spheroids), achieving hydrostatic equilibrium, when their own gravity is sufficient to overcome the structural strength of their material.
It was believed that the cutoff for round objects is somewhere between 100 km and 200 km in radius if they have a large amount of ice in their makeup;[1] however, later studies revealed that icy satellites as large as Iapetus (1,470 kilometers in diameter) are not in hydrostatic equilibrium at this time,[2] and a 2019 assessment suggests that many TNOs in the size range of 400–1,000 kilometers may not even be fully solid bodies, much less gravitationally rounded.
Spheroidal bodies typically have some polar flattening due to the centrifugal force from their rotation, and can sometimes even have quite different equatorial diameters (scalene ellipsoids such as Haumea).
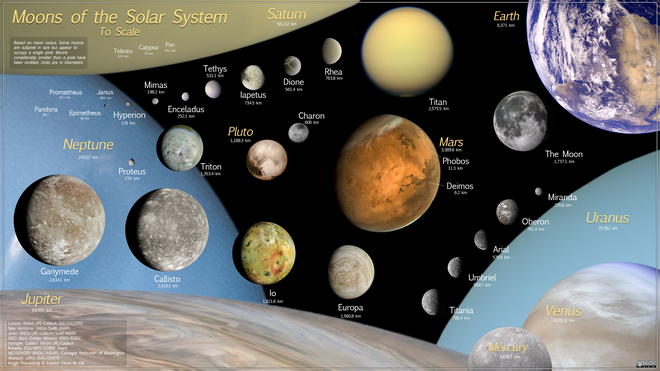
The sizes and masses of many of the moons of Jupiter and Saturn are fairly well known due to numerous observations and interactions of the Galileo and Cassini orbiters; however, many of the moons with a radius less than ~100 km, such as Jupiter's Himalia, have far less certain masses.
For the small outer irregular moons of Uranus, such as Sycorax, which were not discovered by the Voyager 2 flyby, even different NASA web pages, such as the National Space Science Data Center[6] and JPL Solar System Dynamics,[5] give somewhat contradictory size and albedo estimates depending on which research paper is being cited.
There are uncertainties in the figures for mass and radius, and irregularities in the shape and density, with accuracy often depending on how close the object is to Earth or whether it has been visited by a probe.
It was once expected that any icy body larger than approximately 200 km in radius was likely to be in hydrostatic equilibrium (HE).
[9] The known icy moons in this range are all ellipsoidal (except Proteus), but trans-Neptunian objects up to 450–500 km radius may be quite porous.
[10] For simplicity and comparative purposes, the values are manually calculated assuming that the bodies are all spheres.
[57] The known densities of TNOs in this size range are remarkably low (1–1.2 g/cm3), implying that the objects retain significant internal porosity from their formation and were never gravitationally compressed into fully solid bodies.