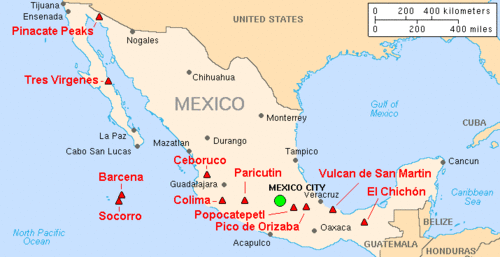
List of volcanoes in Mexico
The diverse array of volcanic features in Mexico includes stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, cinder cones, lava domes, and calderas.
Many of Mexico's volcanoes are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region characterized by frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Mexican volcanoes play a significant role in the country's geography, climate, and culture, influencing local ecosystems, agriculture, and human settlements.
The volcanic activity also poses potential hazards to surrounding communities, necessitating ongoing monitoring and disaster preparedness efforts.
When the lava is eruptive and blows into the air, it separates into small fragments that solidify and fall around the central vent to form an oval cone at the top of the volcano.
The lava from within shield volcanoes is very thin, so when it pours out in all directions from the central summit vent, it travels for long distances.
This is how the Trans-Mexican Volcanic belt evolved and changed and the Rivera plate begin to subduction beneath Central Mexico in the early to late Miocene.
2) The slab tear begins to propagate west to east across the back northern area of the belt, which allowed asthenospheric heat in to generate the Mafic episode.3) The latest Miocene was the onset of more silic volcanics generated by flat slab subduction which pushed the belt further to the north.4) Lastly, The late Pliocene to Holocene is characterized by slab rollback sending the volcanic arc trenchward to the present day position.
Pyroclastic flows, which are toxic gases created by hot clouds that can destroy all things they come into contact with, are another example of a volcanic hazard.
In 2013, It released a cloud of ash that would spread for 2 miles high over a period of several days of eruptions.
In the city of San Pedro Nexapa, about 9.5 from the Popocatépetl, local residents were able to find small piles of ash on parts of the sidewalk.
Following the explosions, a total of 17 flights were canceled “due to climate conditions and in accordance with their own international policies.”[8] Other effects that volcanoes can have on communities in close proximity with the base are more in danger for ash clouds, mud flow, gases, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
This event was one of the largest explosive eruptions in Mexico and produced ash flow deposits up to 40 m thick.